The process of how to get plastic parts made involves four basic steps: come up with a design, decide on a manufacturing process, build a prototype, and then produce the design. Choosing an experienced plastic parts manufacturer who can provide support and feedback through every step of the process increases your chance of success.
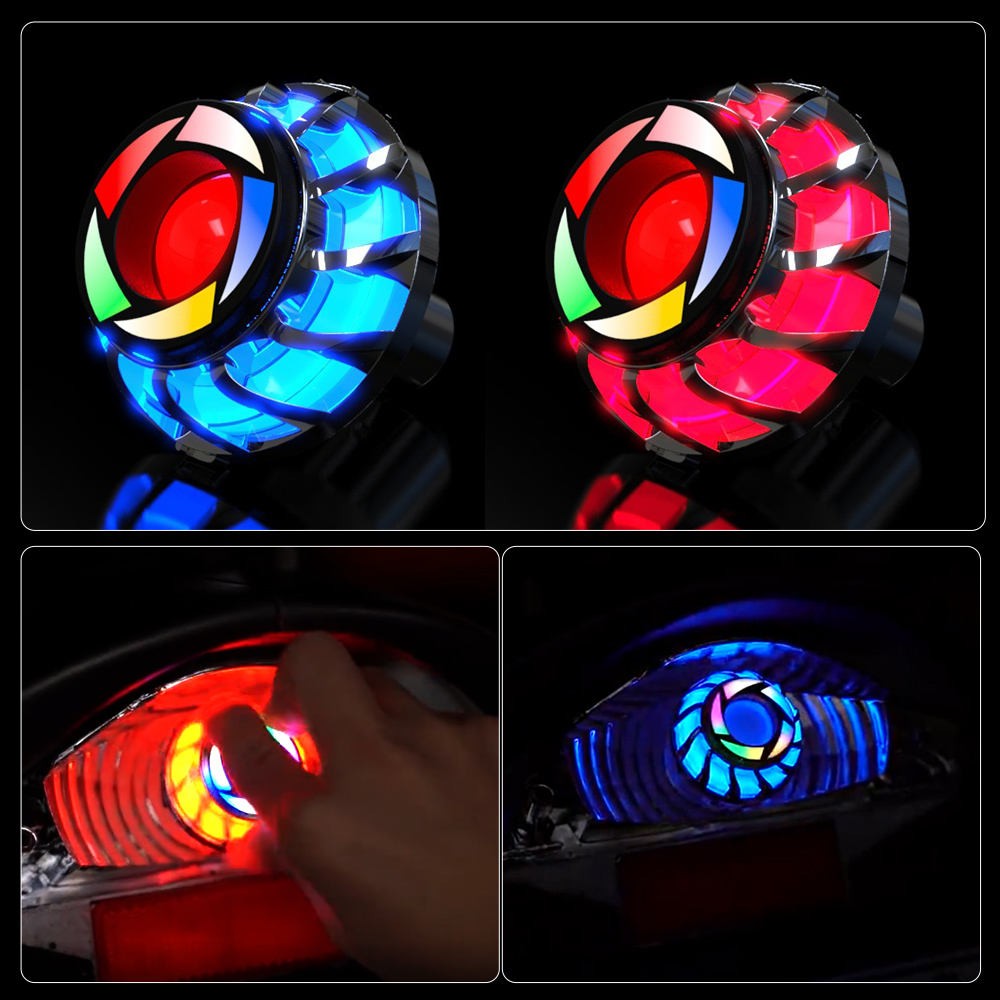
Custom Plastic Parts Cheap Motorcycle Tail Brake Rear Lights Small Batch Injection Molding


How to Get Plastic Parts Made in Four Simple Steps
Come up with a design – The design process isn’t simply sketching up your idea for a part. You must also consider tolerance requirements, material selection, and end-use factors that could affect performance (such as high temperature environments or exposure to corrosive chemicals). At Papler Industry, we offer in-depth consultations with our experienced staff to enhance your original designs. We almost always find a way to improve production without sacrificing quality. You let us know your goal – longer part life, less waste, faster delivery, etc. – and we’ll come up with a solution.
Choose a plastic parts manufacturing process – There are three main ways to manufacture a injection molded plastic parts: CNC machining, injection molding, and additive processing (a.k.a., 3D-printing). While additive processing allows for a high degree of design freedom, it is notorious for poor surface quality and requires post-processing to achieve cosmetic standards and tight tolerances. 3D-printed parts are also limited in the types of plastics they can use. Injection molding has high start-up costs and long lead times, making it a poor choice if you need parts fast. Injection molding is also unable to produce complex geometries in a single part, requiring multiple parts to be produced and then fabricated together. CNC machining, on the other hand, can quickly produce complex parts with tight tolerances and superior surface finishes. There is also greater design flexibility with CNC machining as the machines can quickly be reprogrammed to produce the latest version of your part, minimizing downtime and outdated parts. And CNC machines can handle the most advanced plastics, including PEEK, Vespel, and Ultem.
Build a prototype – Prototypes are the crucial final step before production. Prototypes reveal problems that can only be discovered in real-world applications, allowing you to hone your design as well as determine the efficiency and functionality of the part. CNC machining provides you with a fully functional prototype made from the desired material that meets all tolerance and cosmetic specifications.
Produce the design – Once your design has been vetted and refined through prototyping, it is time to produce your part. Whether you’re starting with a small production run or a large run, Papler Industry will deliver your parts on-time. All of our work is ISO 9001:2008 compliant, and every part goes through our rigorous quality assurance testing process before shipping, which includes 3D measurement, digital microscopic review, optical comparator review and more.


Injection molding is a method of forming a product by injecting molten plastic into a mold and then cooling and solidifying it,which is suitable for mass production and complex shape products.Not only the platic automotive parts, plastic injection parts are used in various industries and our daily life. We offer high quality low cost injection molding services, please contact us for any custom plastic products.
Learn More
Injection molding is one of the most often-used manufacturing processes for creating plastic parts. Thanks to its high-precision, repeatability, and cost efficiency at scale, injection molding is used to make a variety of products and parts from the smallest medical insert up to large automotive & aerospace and defense parts. The injection molding process requires an injection molding machine, raw plastic material, and a machined mold. The raw plastic material is first melted in the injection unit and is then injected into the mold — most often machined from steel or aluminum — where it cools and solidifies into the final plastic part. The key steps in the injection molding process are clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection.
Learn More
Papler industry main services offering include insert-molding, overmolding & two color injection molding, as well as with CNC machining. With more than 10 years of experience, Papler industry are able to produce custom affordable injection molding parts plastic, insert molding parts and overmolding parts according to customers’ specifications, drawings or samples.
Learn More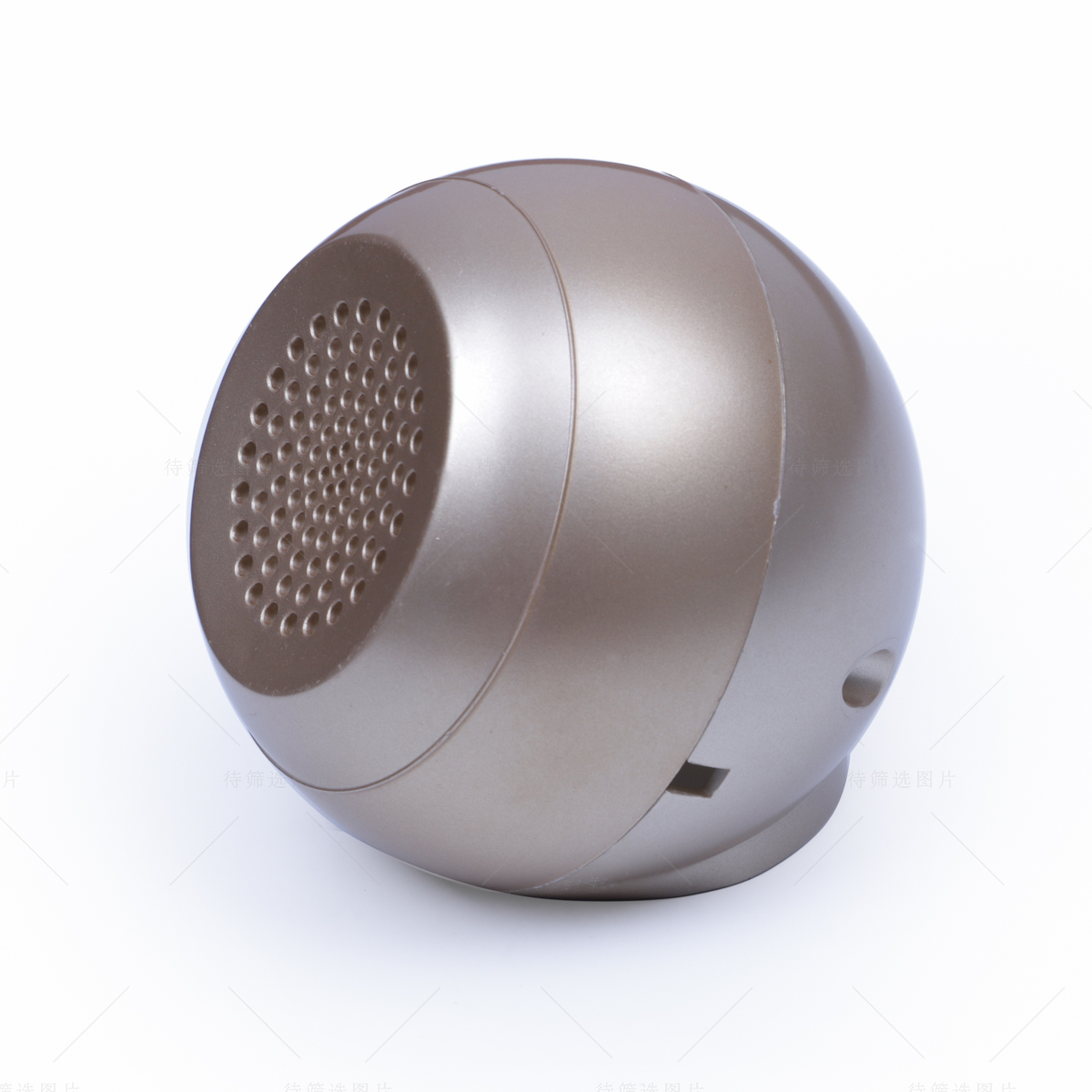
Injection molding & injection moulding is the most commonly used manufacturing process for manufacturing plastic parts. It refers to the method that under a certain temperature, the plastic material completely melted by screw stirring is injected into the mold cavity with high pressure, and then cooled and solidified to obtain the injection molded product. This method is really cost effective and it’s suitable for the mass production of complex shape parts. There are mainly six stages: mold closing, glue injection, pressure maintaining, cooling, mold opening and product removal. Molding also has the highest variety of materials, colors, and configurations when compared to CNC machining or even 3D printing. Beyond materials, injection molded parts can have custom cosmetics, polishes, or surface textures.
Learn More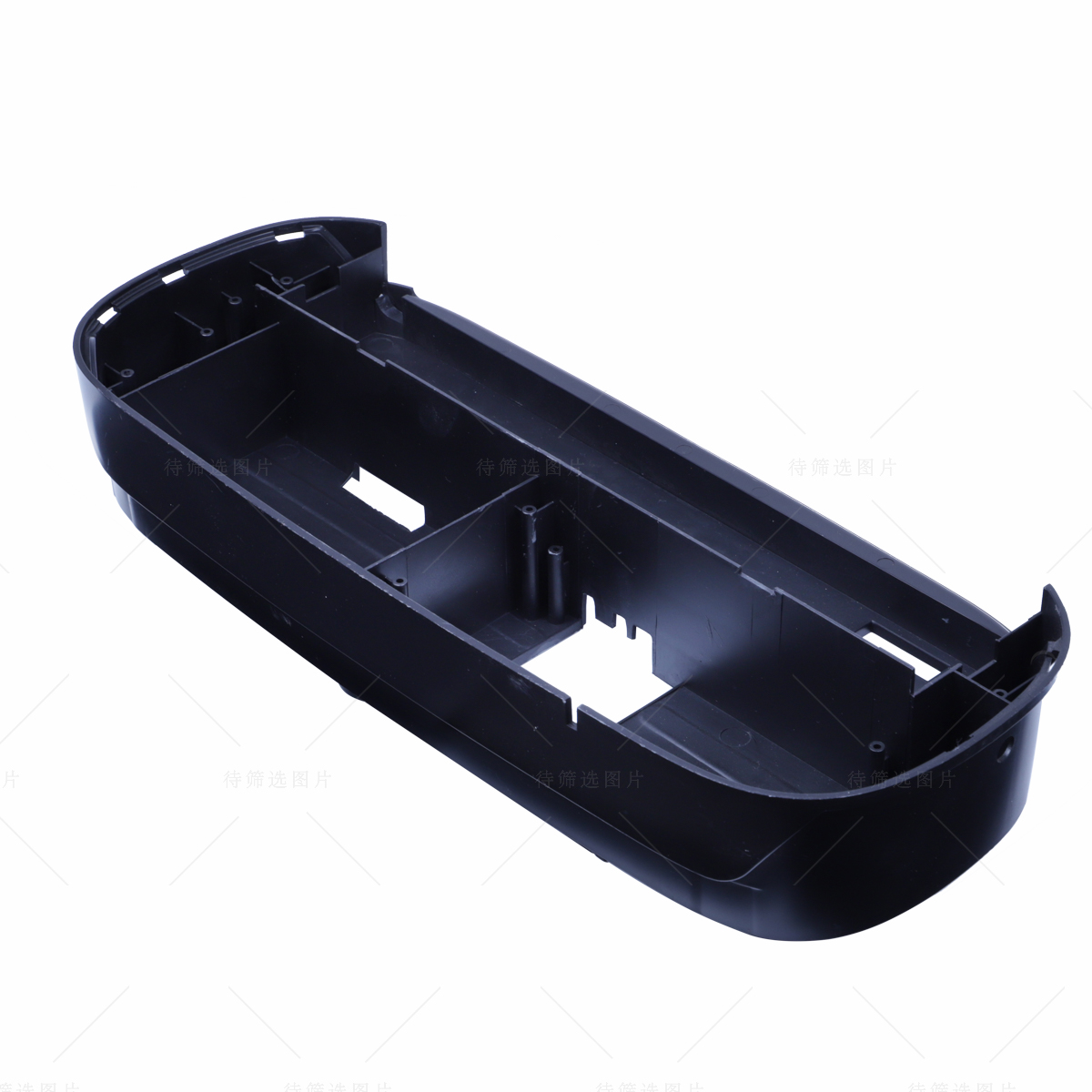
Injection molding is manufacturing process, in which a molten material in injected into a mold under high pressure. Then it is cooled and solidified to get the final product.When you need to make highly efficient mass products at faster rates then injection molding is one of the best technique to get things done. It is amongst the most trusted methods for manufacturing plastic parts and it offers many lucrative manufacturing friendly properties. It is widely used in many industries due to its excellent attributes like capability to make complex part designs, huge material and color options, enhanced strength and many others.
Learn More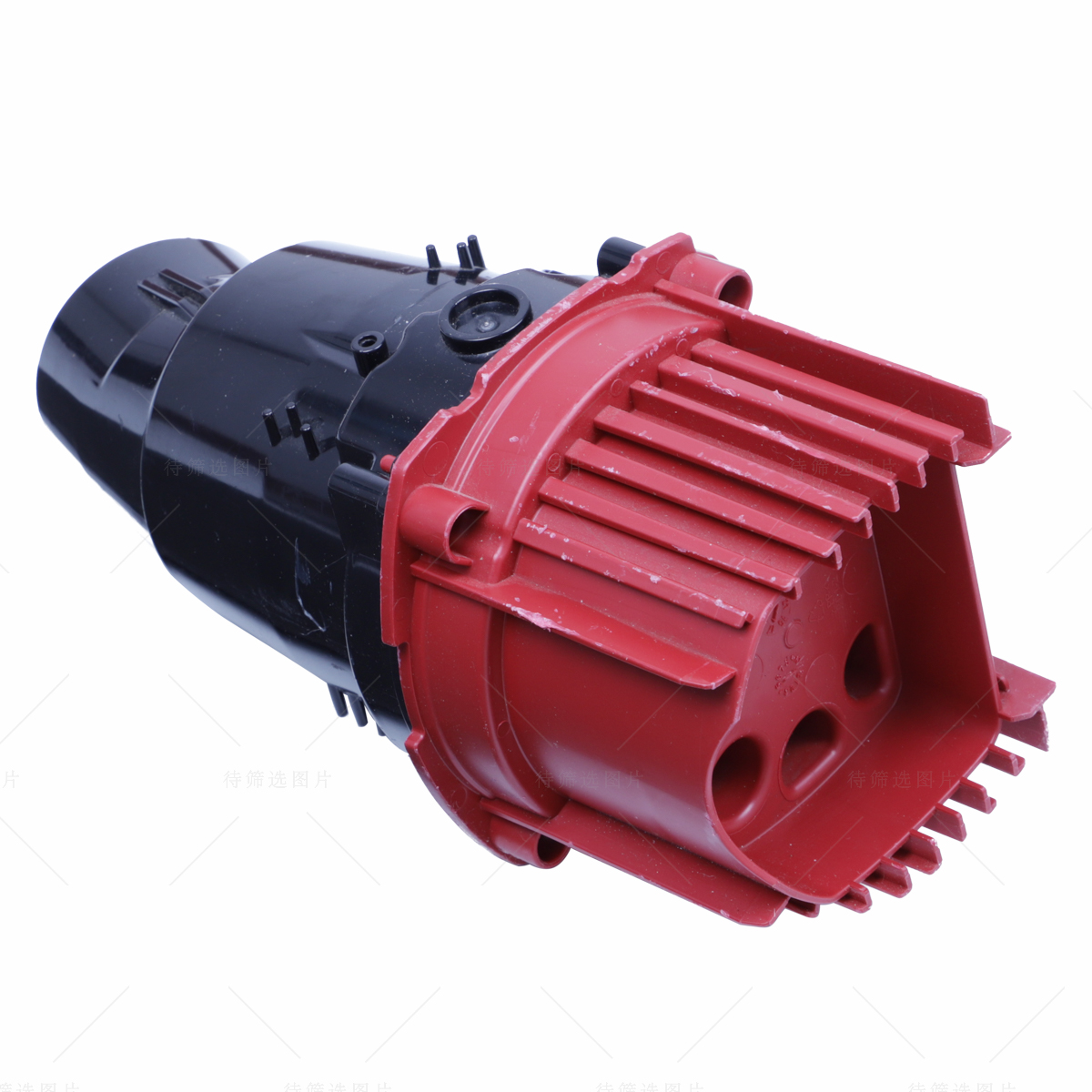
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity.
Learn More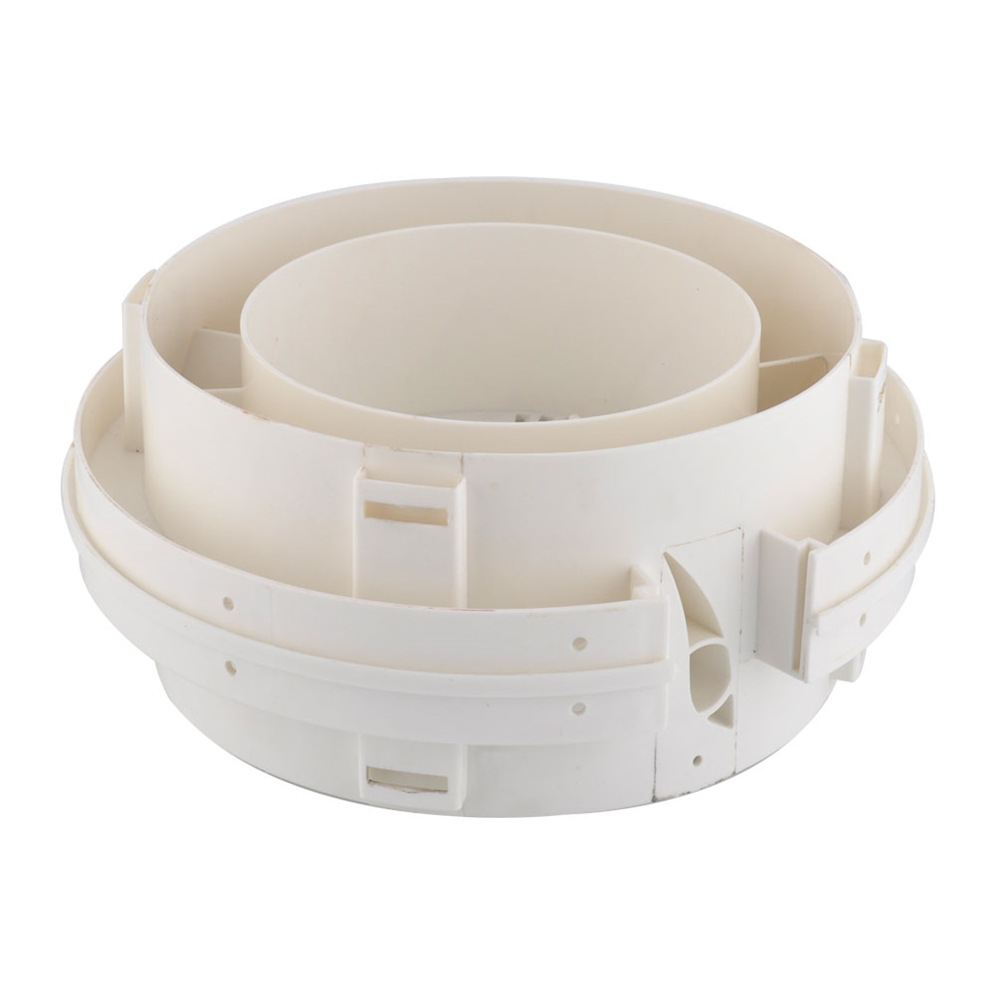
Injection moulding uses a special-purpose machine that has three parts: the injection unit, the mould and the clamp. Parts to be injection-moulded must be very carefully designed to facilitate the moulding process; the material used for the part, the desired shape and features of the part, the material of the mould, and the properties of the moulding machine must all be taken into account. The versatility of injection moulding is facilitated by this breadth of design considerations and possibilities.
Learn More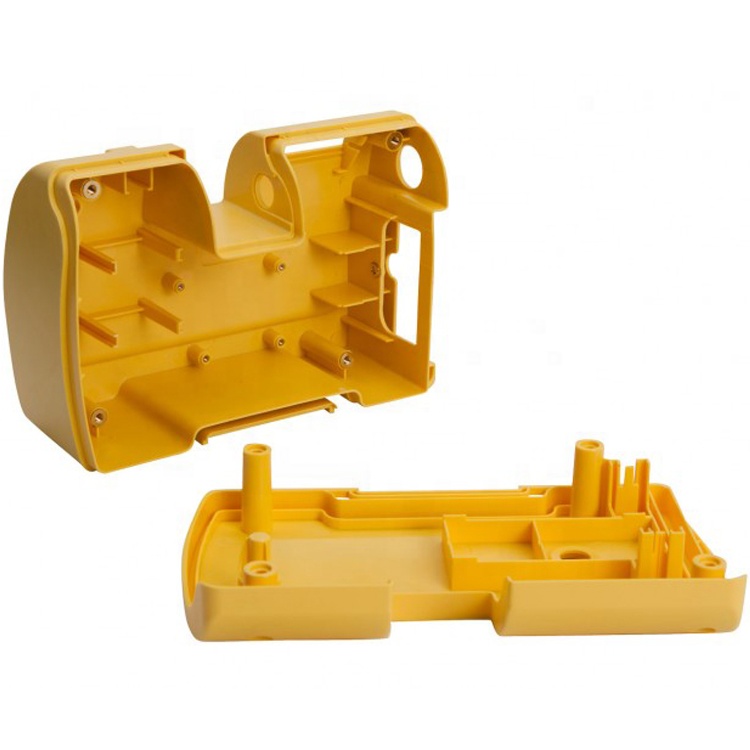
Injection Molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts in large volume. It is most typically used in mass-production processes where the same part is being created thousands or even millions of times in succession.
Learn More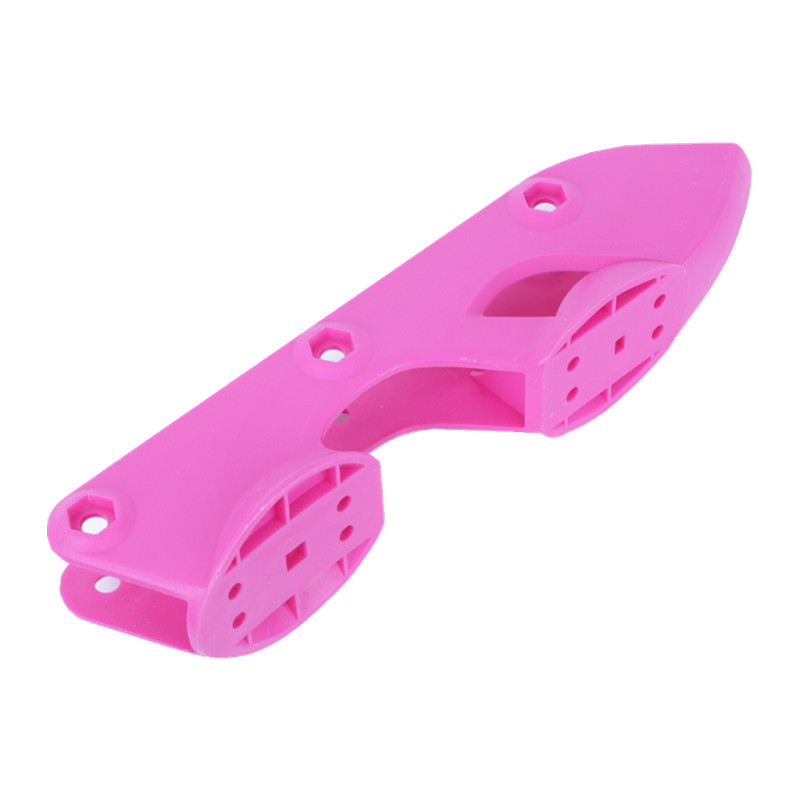
Injection molding is a method to obtain molded products by injecting plastic materials molten by heat into a mold, and then cooling and solidifying them. The method is suitable for the mass production of products with complicated shapes, and takes a large part in the area of plastic processing.
Learn More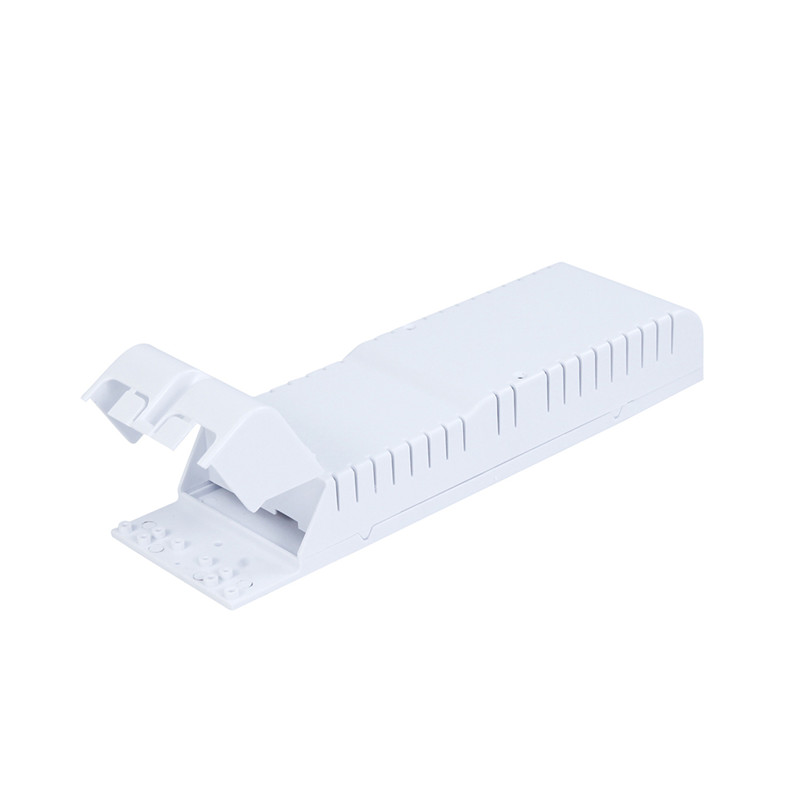
Prototype plastic injection molding is the process used to produce low or high volumes of custom plastic parts for commercial and industrial use. From intricate automobile safety components to simple products like business card holders, the applications span a range of industries. Our injection molding experts look forward to working with you on your mold build project as the next step toward manufacturing your custom molded parts.
Learn More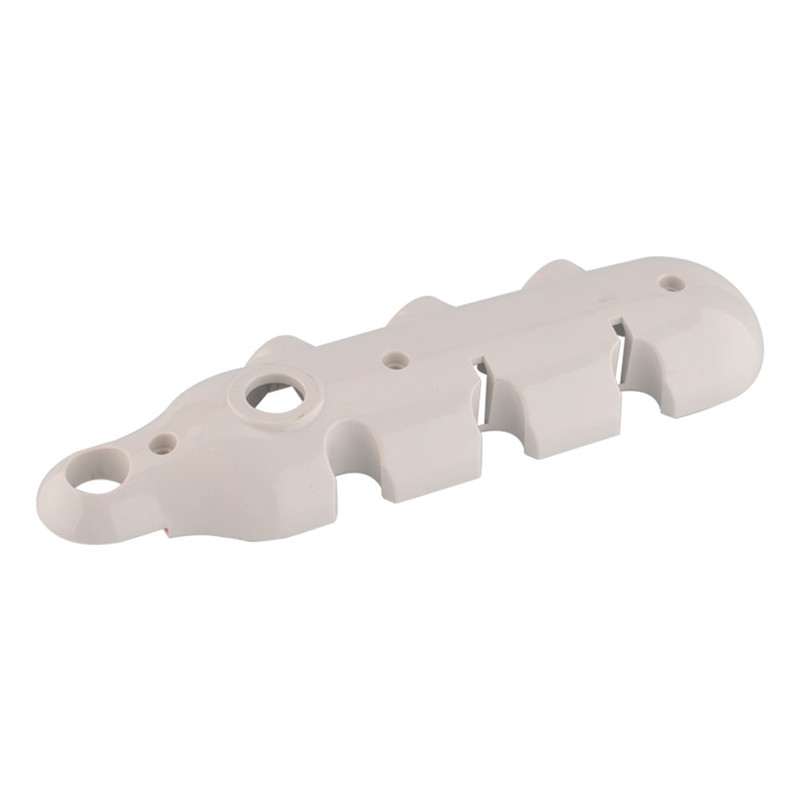
Injection plastic molding has a low cost of production, produces highly accurate plastic parts, and can work with any thermoplastic material. Injection molding can handle most production run volumes, produce parts of varying sizes, and is highly repeatable.
Learn More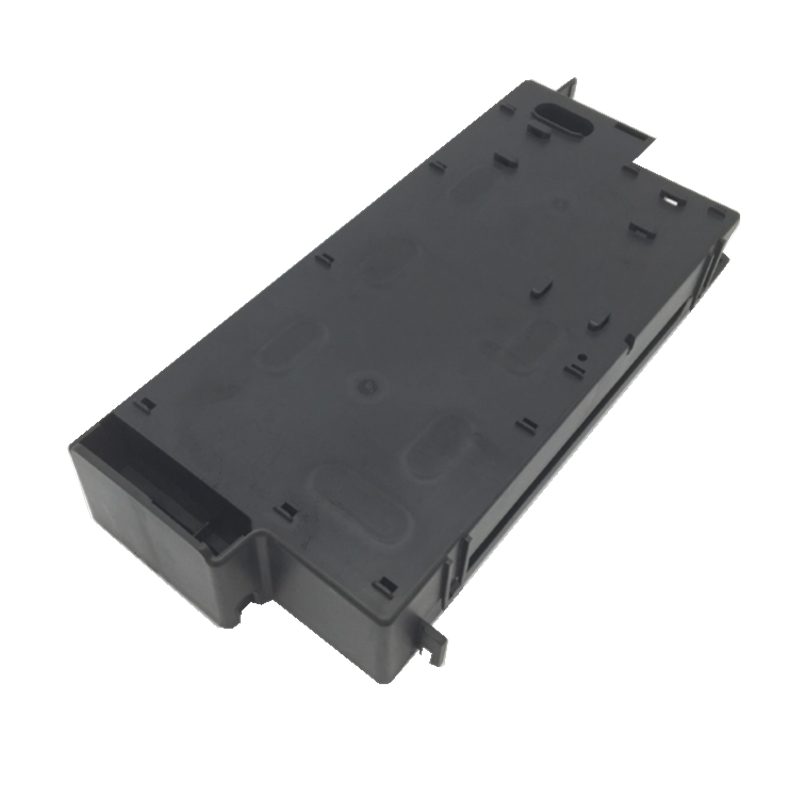
Plastic parts and components are known to reduce costs and boost efficiencies in many industries – but nowhere are the advantages of plastics more evident than in the automotive plastic parts industry. Plastics offer increased fuel efficiency, improved corrosion resistance, greater design flexibility, superior durability, higher performance and lower costs. Remarkably malleable, plastics are also strong enough to hold their structure and shape.
Learn More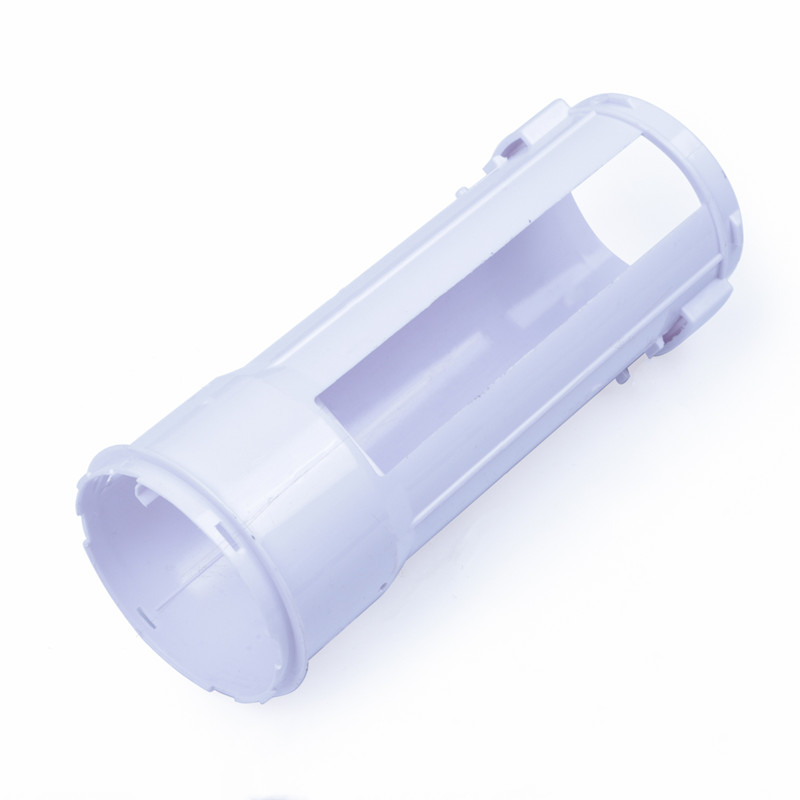
3D printed injection mold tooling enable designers to print and mold multiple iterations of a part. This gives them freedom to explore many more designs and confidence that their final design will be the right design.
Learn More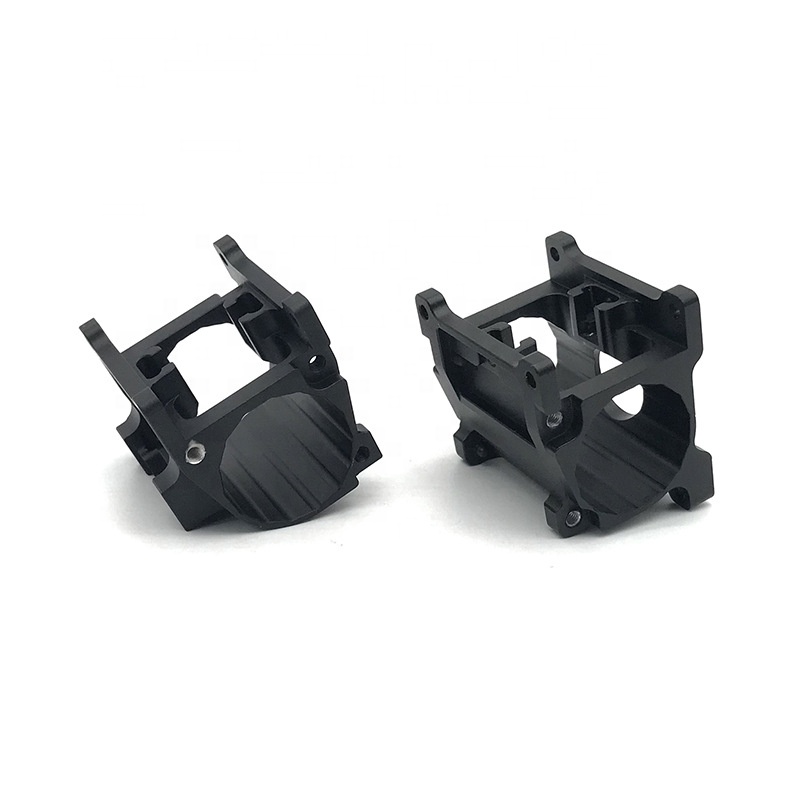
plastic injection molded is a manufacturing process that allows for parts to be produced in large volumes. It works by injecting molten materials into a mould. It is typically used as a mass production process to manufacture thousands of identical items. Injection moulding materials include metals, glasses, elastomers and confections, although it is most commonly used with thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
Learn More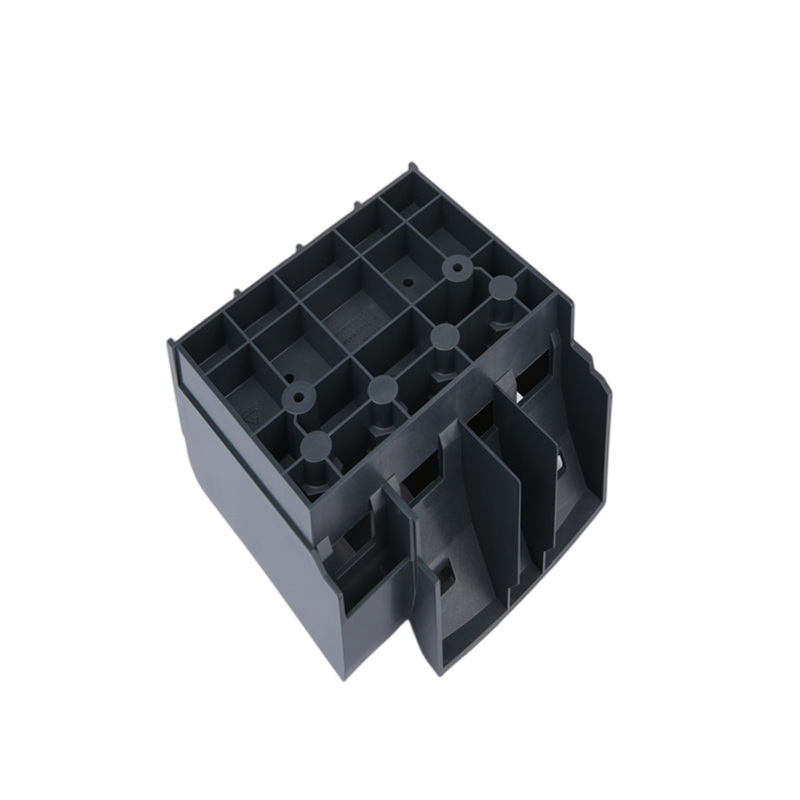
Papler Industry Co.,Ltd have two plastic injection moulding service options - prototyping and on-demand manufacturing - with each offering their own benefits depending on your project needs. If part quantities are higher, an affordable piece - part price is important and quick - turn production throughout the product life cycle is critical. For this our on-demand manufacturing option is ideal.
Learn More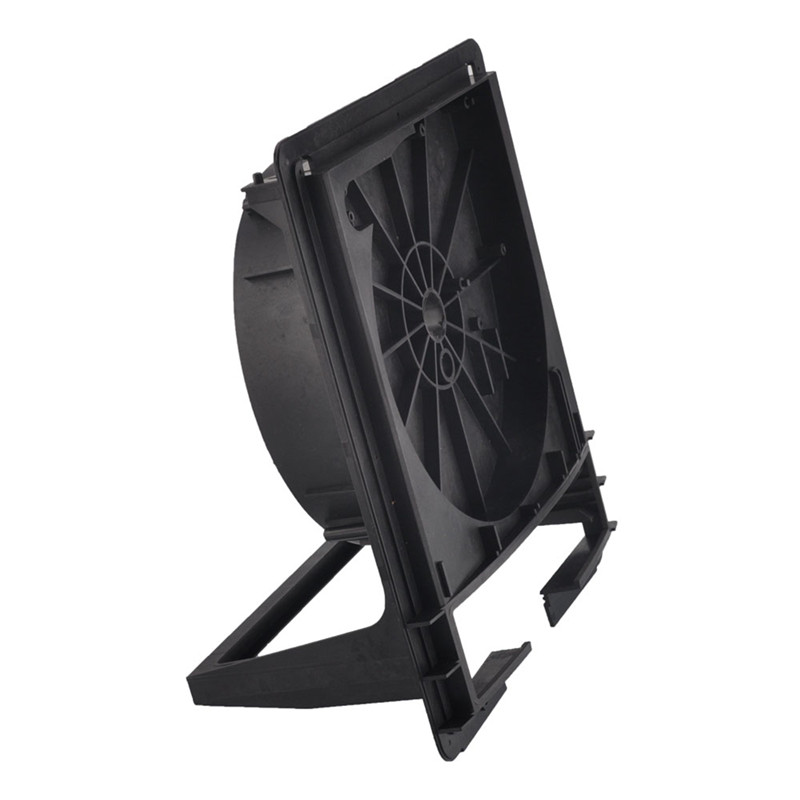
plastic injection molding is an invaluable process for creating plastic parts. This process is fast, cheap, and helps create vast volumes of identical objects. One of the most significant advantages of injection molding is the natural surface finish of molded parts. Even without any injection molding surface finish or post-processing treatment, molded parts have smooth surface finishes suitable for many end uses.
Learn More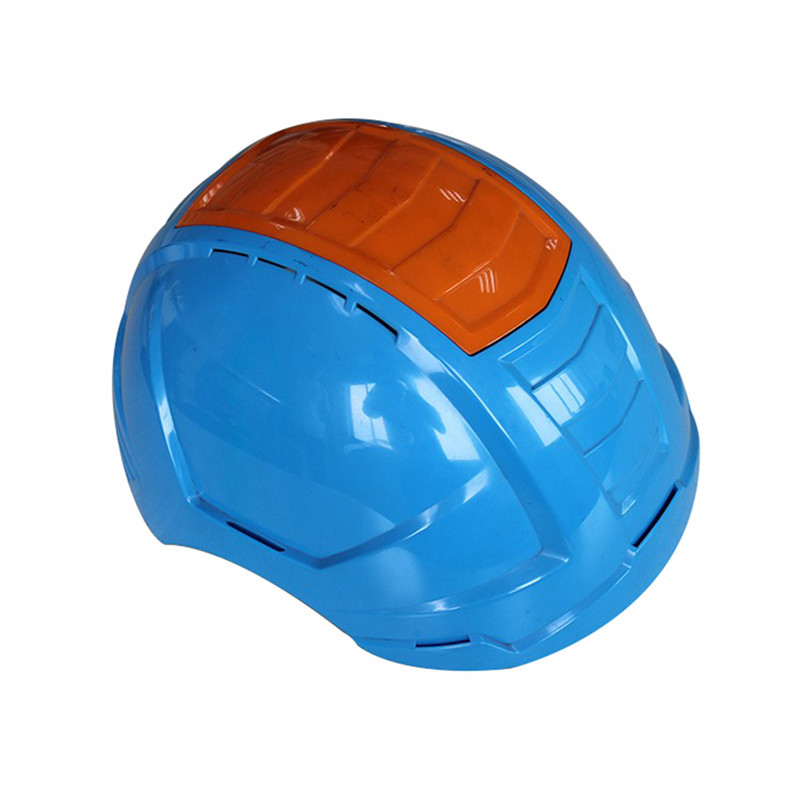
Papler Industry Co.,Ltd has been providing high quality plastic injection moulded products. The design of plastic products, construction of extremely high quality plastic injection molds and technical expertise in plastic injection molding are the DNA of our company. From helping customers design their custom plastic parts to offering small and high volume custom injection molding, prototype injection molding and insert molding services, we continuously enhance our capabilities through customer needs.
Learn More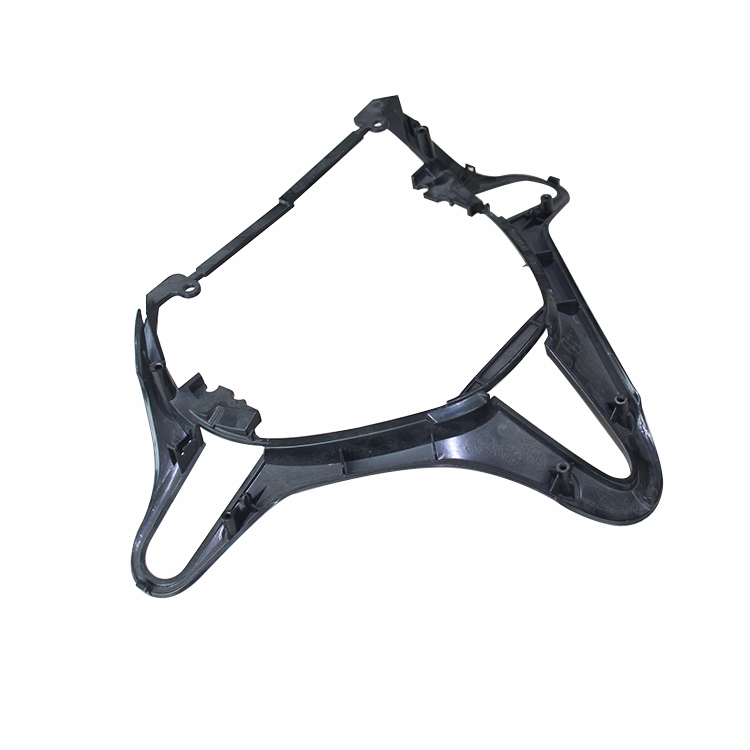
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process where resin in a barrel is heated to a molten state, then shot into a mold to form a final production-grade thermoplastic part.
Learn More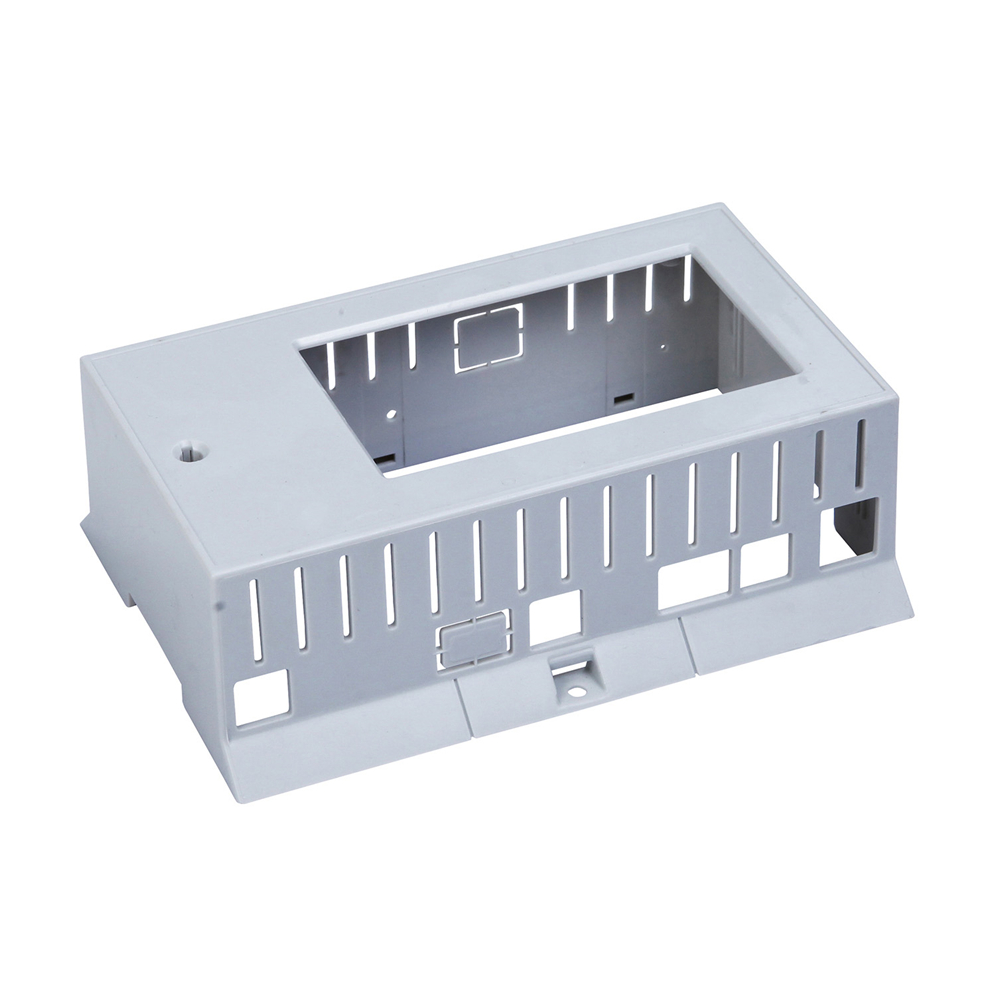
Plastic injection molding is the most commonly used process for manufacturing plastic parts. This process enables high production rates, offers repeatable high tolerance, allows flexibility to create complex shapes, and exhibits low labor costs. Graphics may be added by combining plastic injection molded parts with painting and laser etching.
Learn More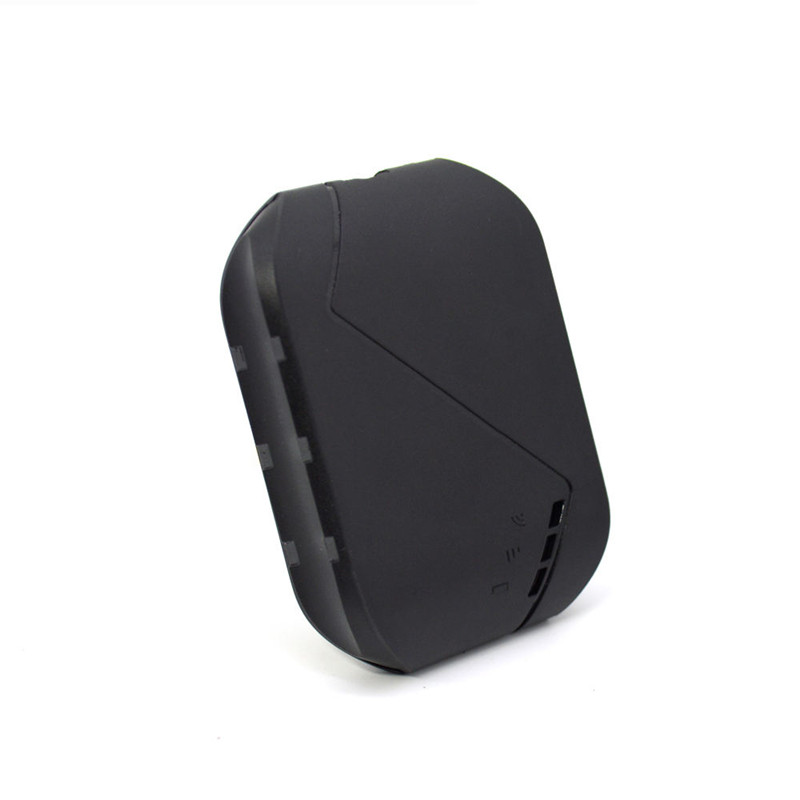
Plastic electronic boxes and enclosures are designed for a variety of electronic equipment, including audio transmitters, video transmitters, game machines, remote control devices, test equipment, and more. These enclosures are made of ABS plastics and feature an exceptional durability. With a complete range of production equipment and strict attention to manufacturing processes, including mold design, injection molding, assembly, and more, we guarantee the enclosure precision. We also offer customized plastic electronic boxes and enclosures to meet special requirements.
Learn More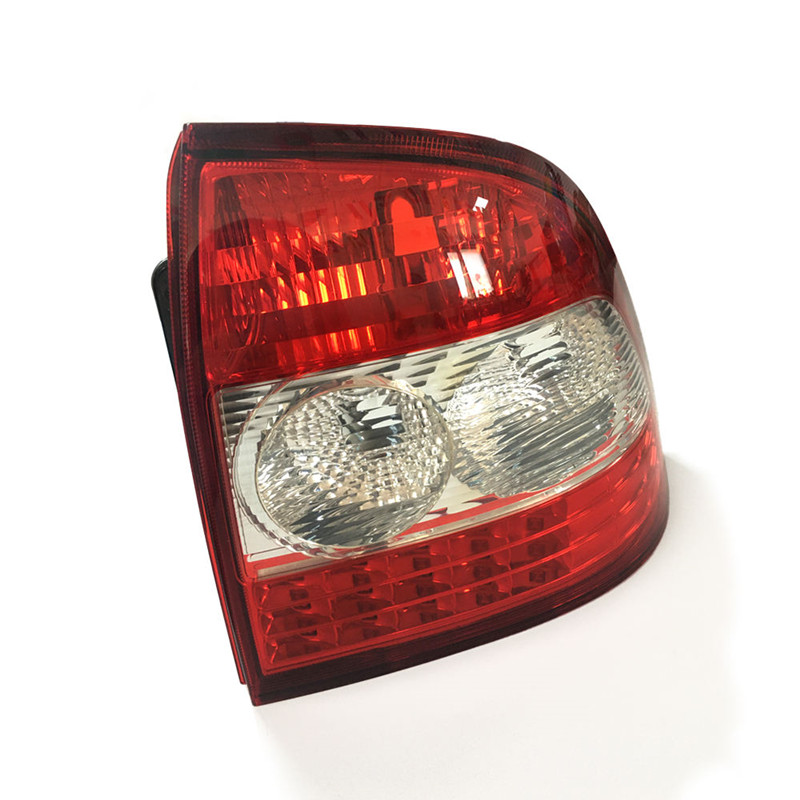
Functionally and aesthetically, lighting is essential for automotive. Modern lighting is not only serving proper vision for the driver, but also contributing to enhance safety by adaptive lighting technology combining with advanced driving assistance systems. Papler Industry Co.,Ltd is offering various solutions to plastic vehicle headlight.
Learn More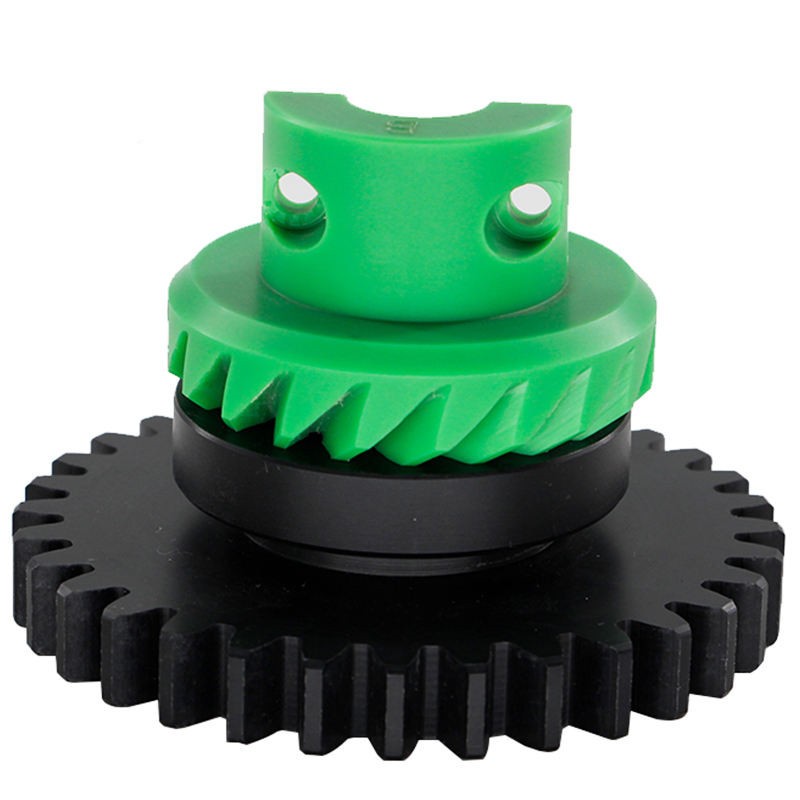
Plastic injection moldings is rapid delivery of prototype, bridge and production injection molding including over-molding, insert-molding, and cast urethane.
Learn More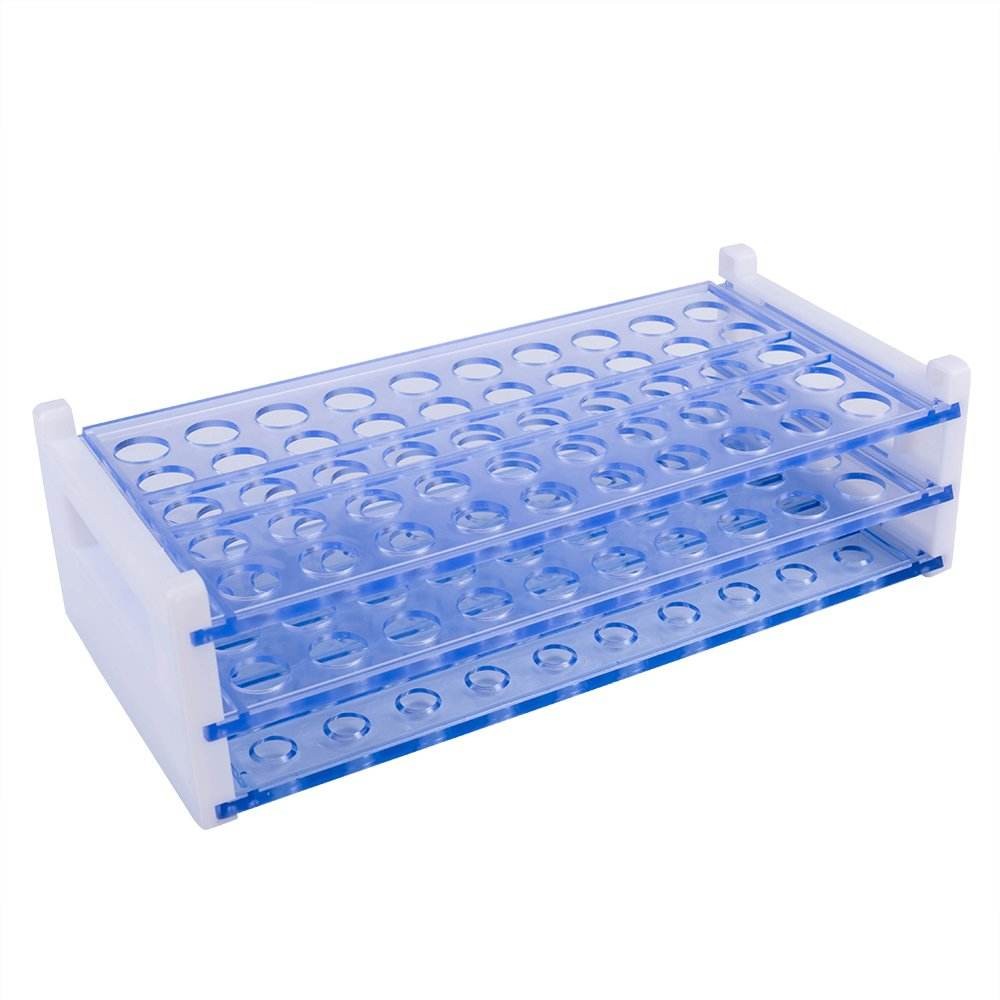
Thermoplastic plastic injection moulding is a manufacturing process that creates fully functional parts by injecting plastic resin into a pre-made mold. It has several sub categories, such as rapid injection molding, which is best utilized in fine tuning prototypes prior to a product being given the go-ahead for production. Another sub category, production injection molding, is best utilized for full product runs.
Learn More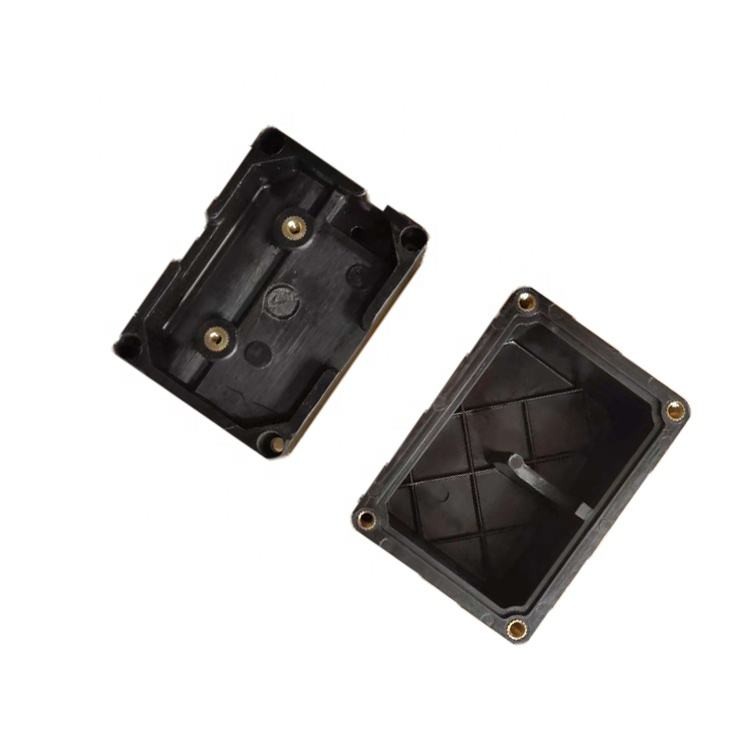
Developers utilize the thermoplastic injection molding process for many applications, as it can produce anything form car door panels to cell phone cases with good accuracy and surface finish. What's more is that it's the industry standard for producing plastic mould parts, so developers can be certain they're putting out a quality product if they go this route in the development process.
Learn More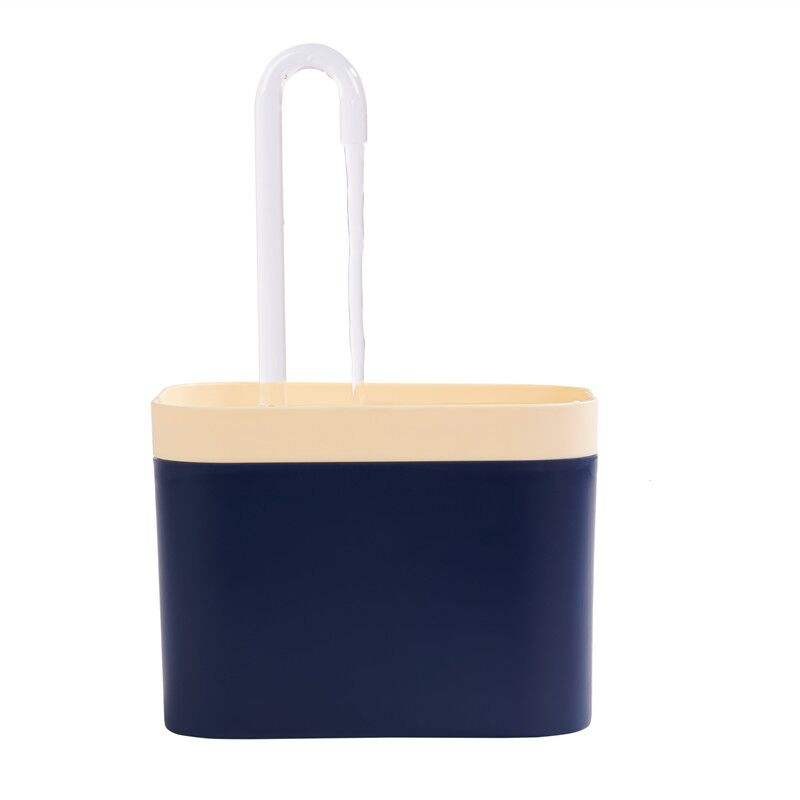
Injection molding is a process in which plastic pellets are melted and injected under high pressure into a mold cavity. The molded parts are then ejected, and the process repeated.The finished products can then be used as is, or as a component of other products.
Learn More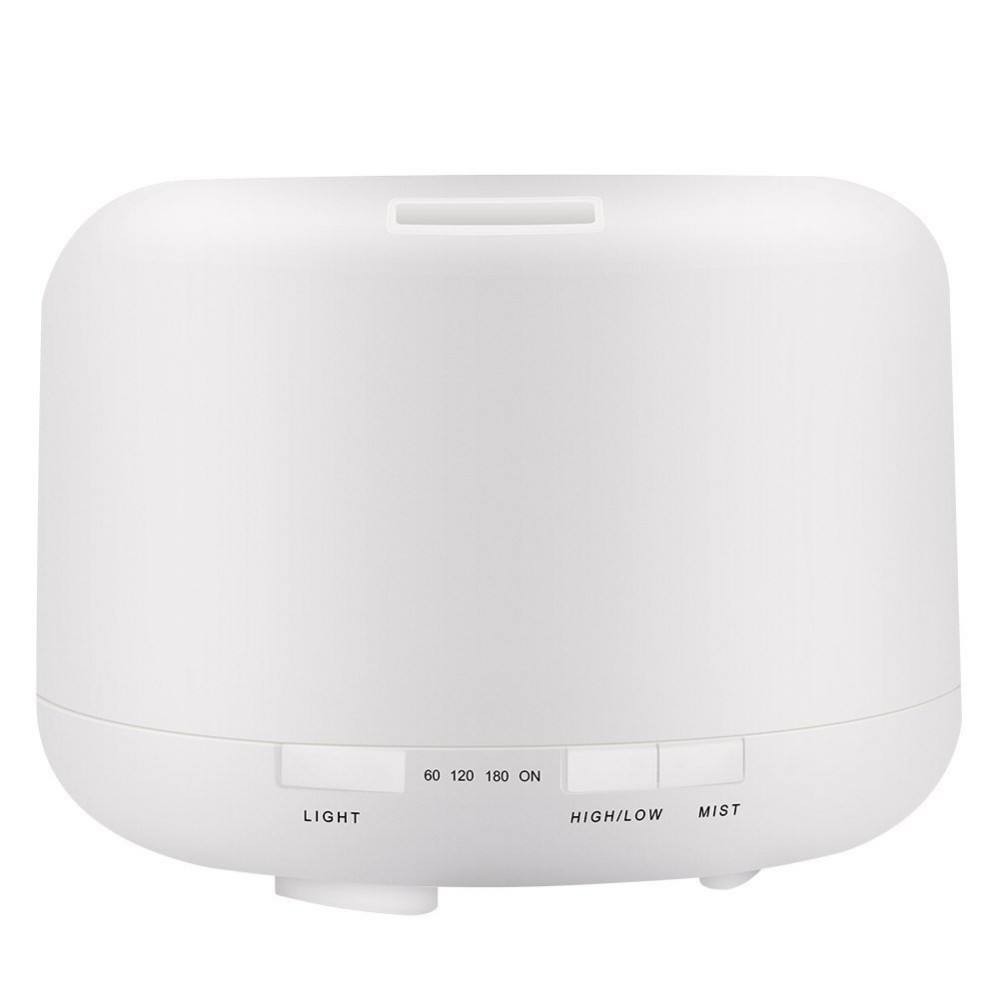
Injection molding utilizes very high pressures and typically the machine is hydraulic or, increasingly, electric. Tooling for production injection molding applications must be able to survive under high pressure and is made from steel or aluminum. The potential high cost of tooling often drives the economics of a plastic molding application. Injection molding is an effective way to make custom parts.
Learn More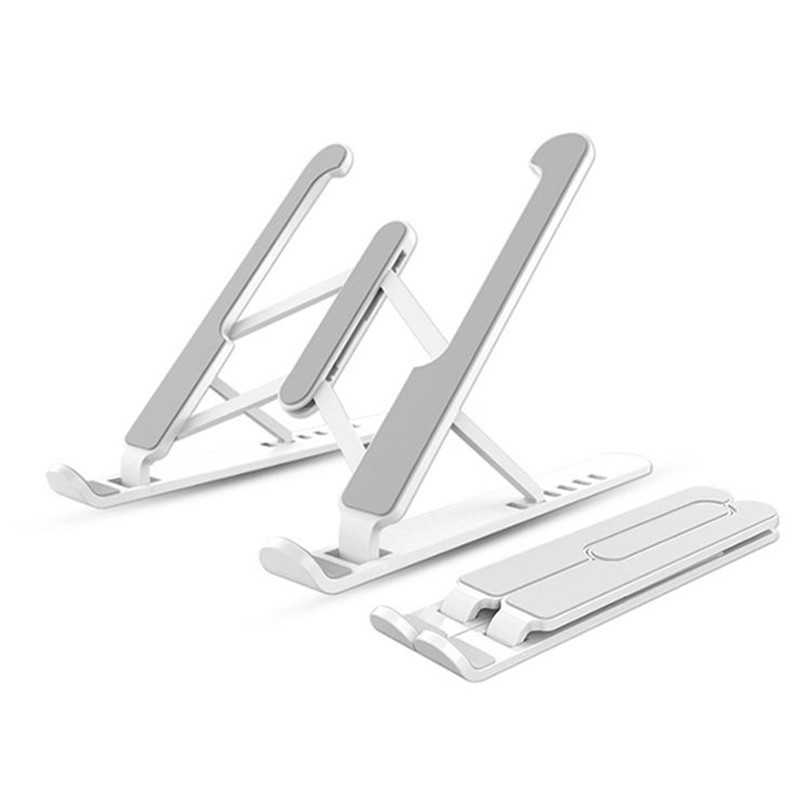
Injection molding is A mold is made based off a CAD file. That's the laborious part of the process as it takes time to create the mold. Such molds are typically made from aluminum or steel.After the mold is created, the thermoplastic resin is injected into it and then left to cure and form the part. The material is first fed into a heated barrel before being launched into the mold to cold and cure.Following curing, the part is removed from the mold and the process starts over until the part run is completed.
Learn More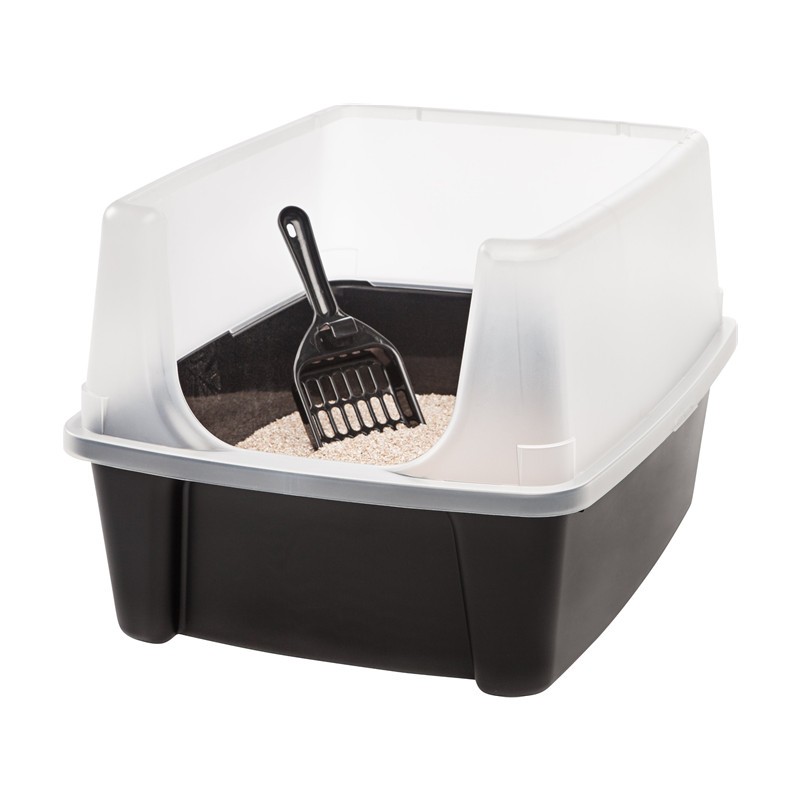
Injection molding is one of the most versatile traditional manufacturing methods, creating complex, durable, and reliable parts. Injection molding produces parts that serve an array of purposes.
Learn More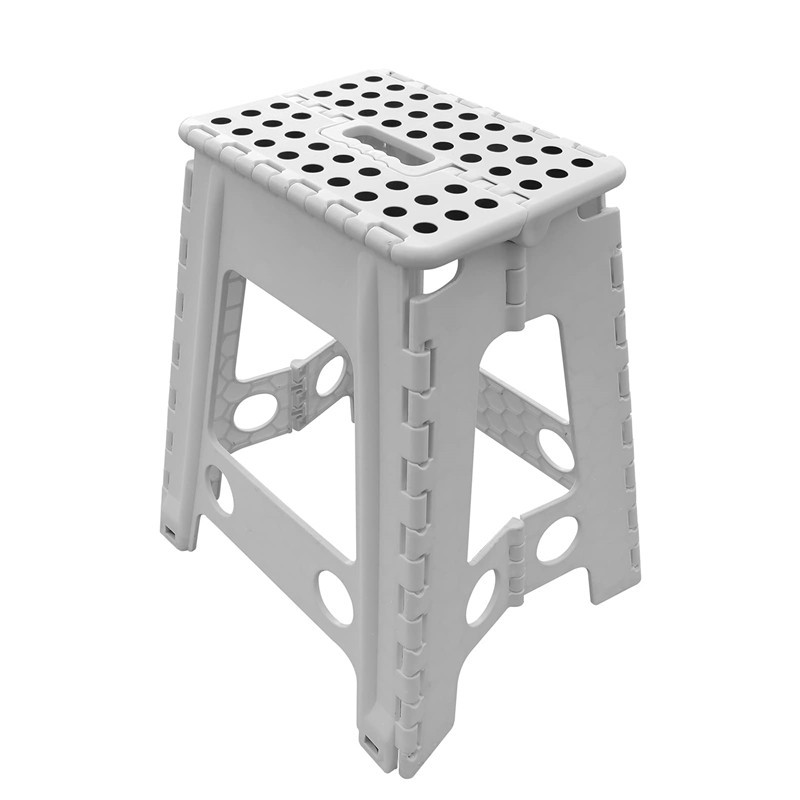
Once a mold is created, injection molding produces parts incredibly fast, making it an ideal method for high-volume production.
Learn More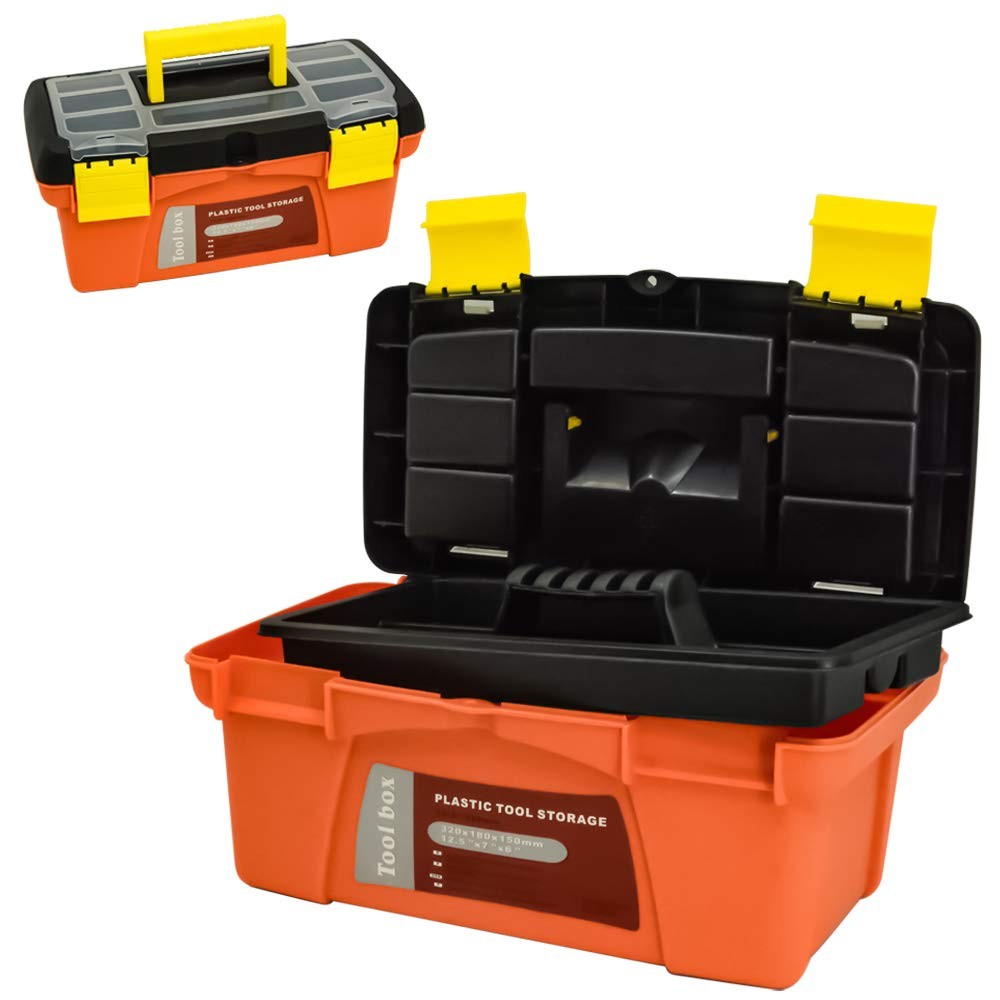
With a wide variety of plastics to choose from, injection molding is a flexible process capable of producing parts for a variety of industries.
Learn More
The process of how to get plastic parts made involves four basic steps: come up with a design, decide on a manufacturing process, build a prototype, and then produce the design. Choosing an experienced plastic parts manufacturer who can provide support and feedback through every step of the process increases your chance of success.
Learn More
Papler Industry provides plastic injection molding services to many industries inluding consumer products, appliances and house wares, OEM’s, packaging, toy, furniture, and the hosiery and garment industry.
Learn More
Plastic enclosures are designed to house and protect sensitive electronic and electrical components in a variety of applications. Our high-quality and durable plastic housings are molded from flame-retardant ABS or impact-resistant polycarbonate for indoor or outdoor applications that require non-metallic enclosures. Available in an array of sizes, shapes and colors, our selection ensures you can find the right solution for any application.
Learn More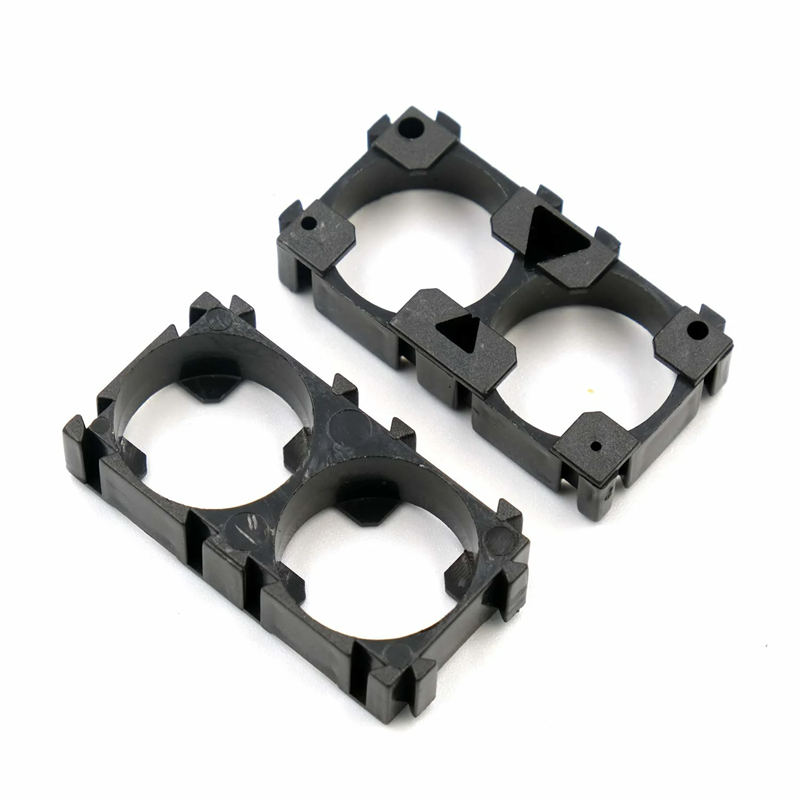
Plastic enclosures are designed to house and protect sensitive electronic and electrical components in a variety of applications. Our high-quality and durable plastic housings are molded from flame-retardant ABS or impact-resistant polycarbonate for indoor or outdoor applications that require non-metallic enclosures.
Learn More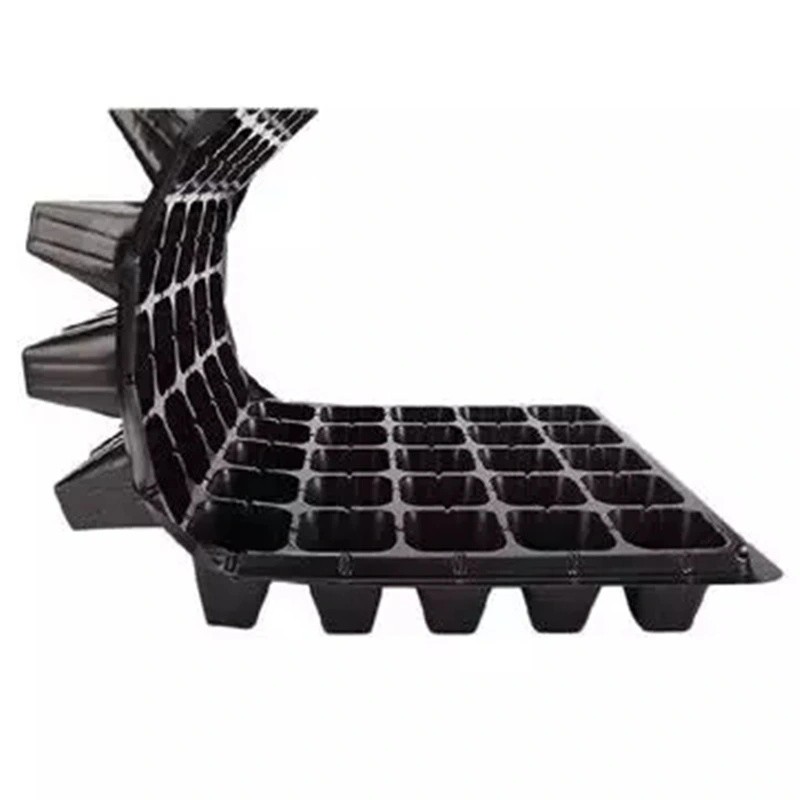
Injection molding creates many of the plastic containers and tubs in which consumer products are packaged. Other injection molded products found in many households include drinkware, bottlecaps,planting containers,barbeque accessories, toilet seats and outdoor furniture. The plastics used in injection molding are very durable for repetitive use and hold up well to weather and temperature variations for outdoor applications.
Learn More
Injection-molded products are widely used in all fields of the national economies, such as transportation, packaging, post and telecommunications, communication, construction, home appliances, computers, aerospace, defense, etc. They have become indispensable means of production and consumer goods.
Learn More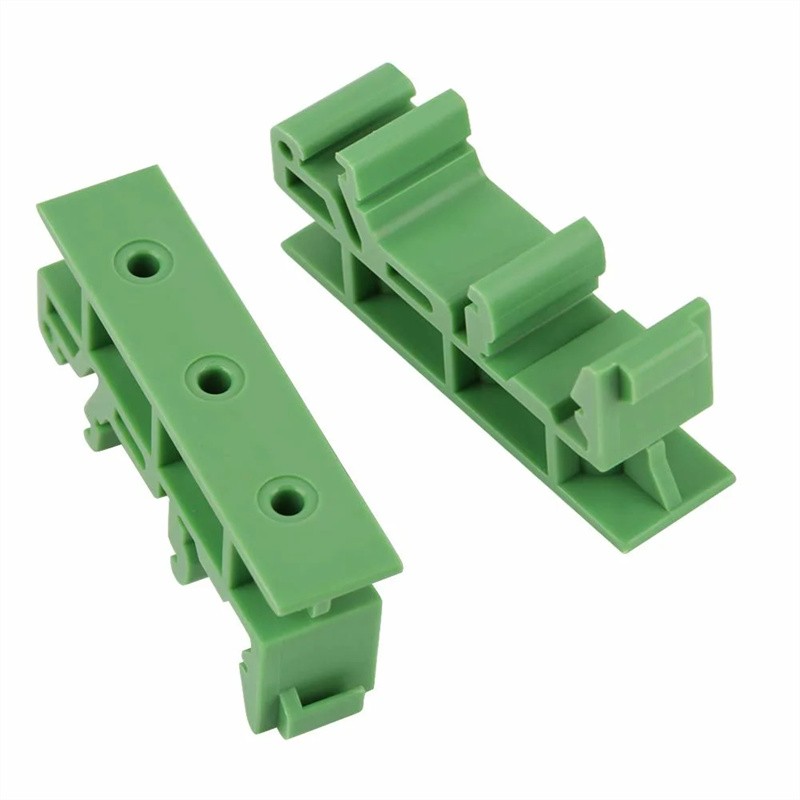
Plastic injection molding machines with injection molding products are a relatively wide variety and wide range of applications, especially in the equipment and automotive manufacturing industry, there are a variety of shape injection molding products for accessories.
Learn More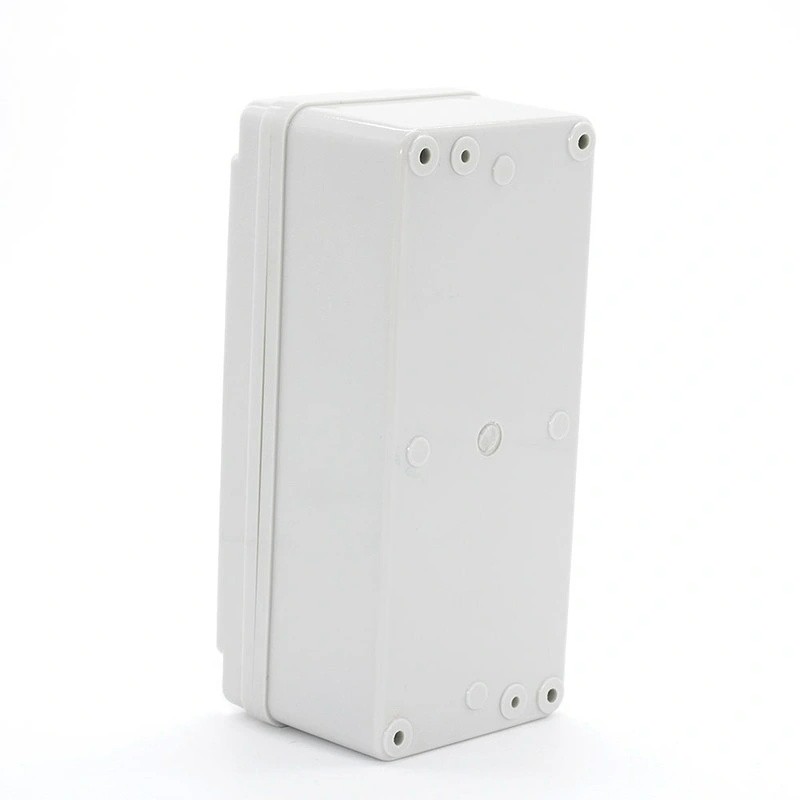
Plastics are ubiquitous, and manufacturers employ different methods when making plastic products. One of the most popular among these methods is injection molding. Besides, manufacturers use this process because it is cost-effective and aids in producing high-quality parts.
Learn More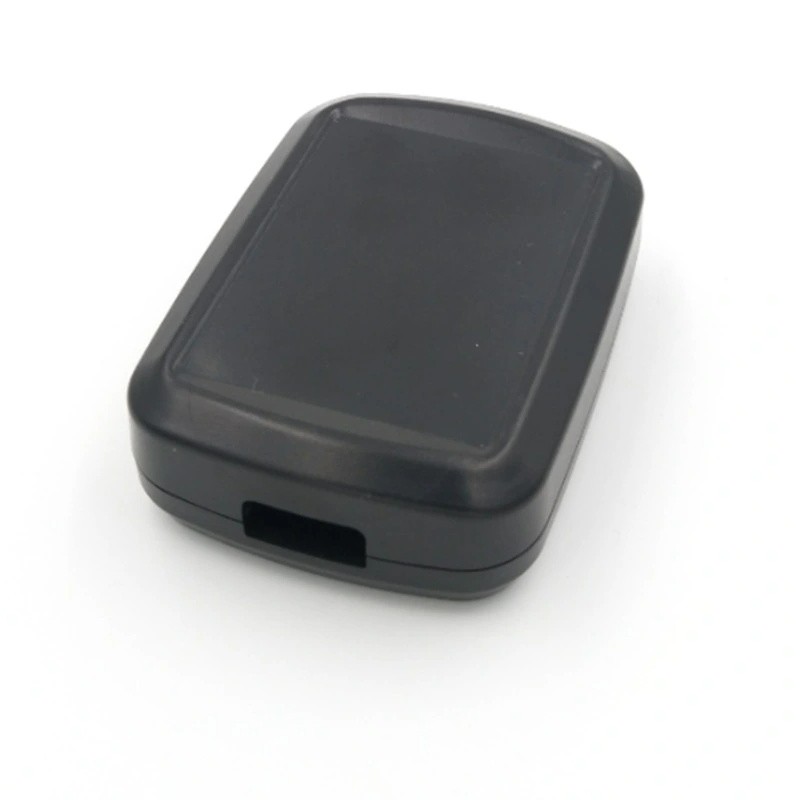
Although plastics do not conduct electricity, they still have a place in the electronics industry. This industry employs injection molding to produce electrical face plates and other electronic devices. Besides, plastics used by manufacturers in the electronics industry are often durable with excellent resistance to electricity. Injection molding applications include the production of remote controls, computers, medical instruments, televisions, key fobs, etc.
Learn More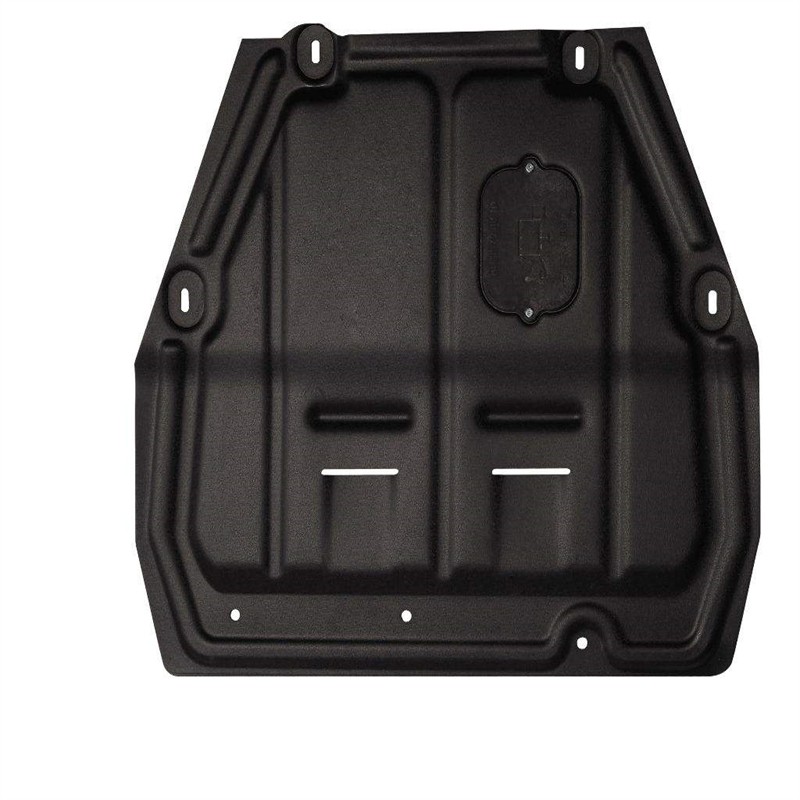
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More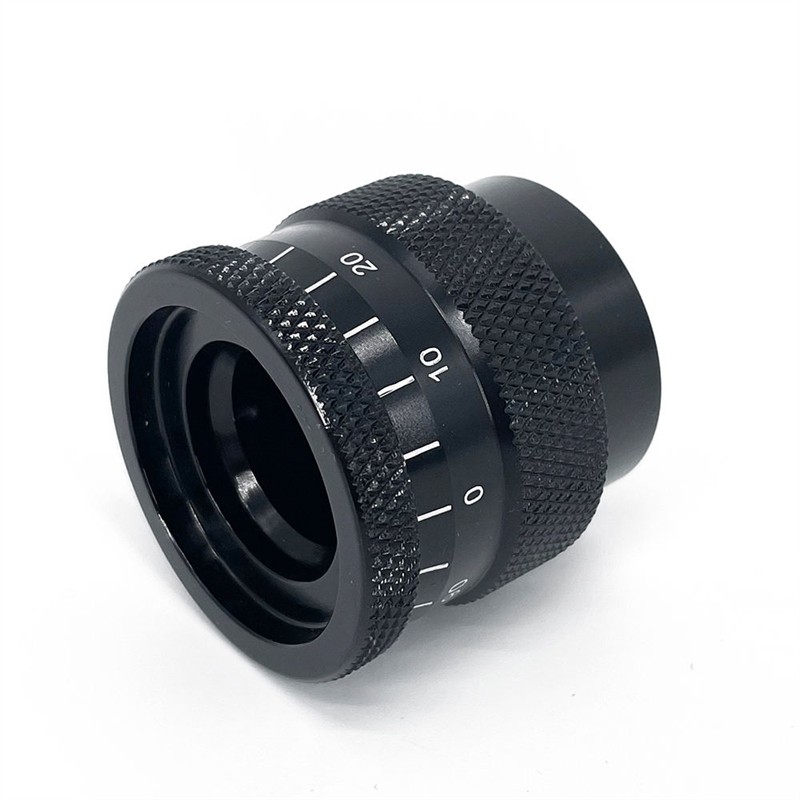
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More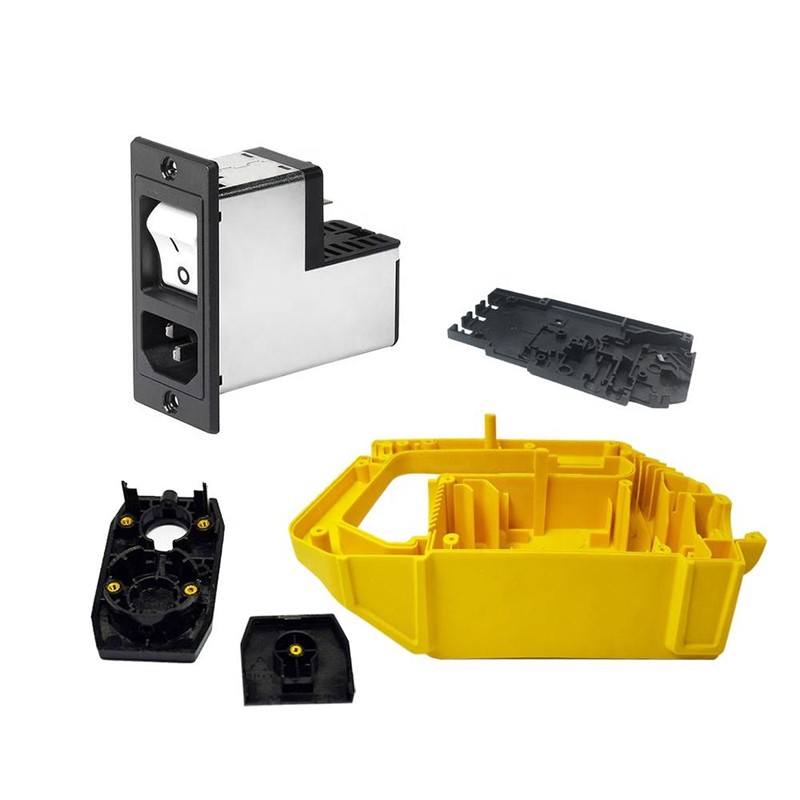
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More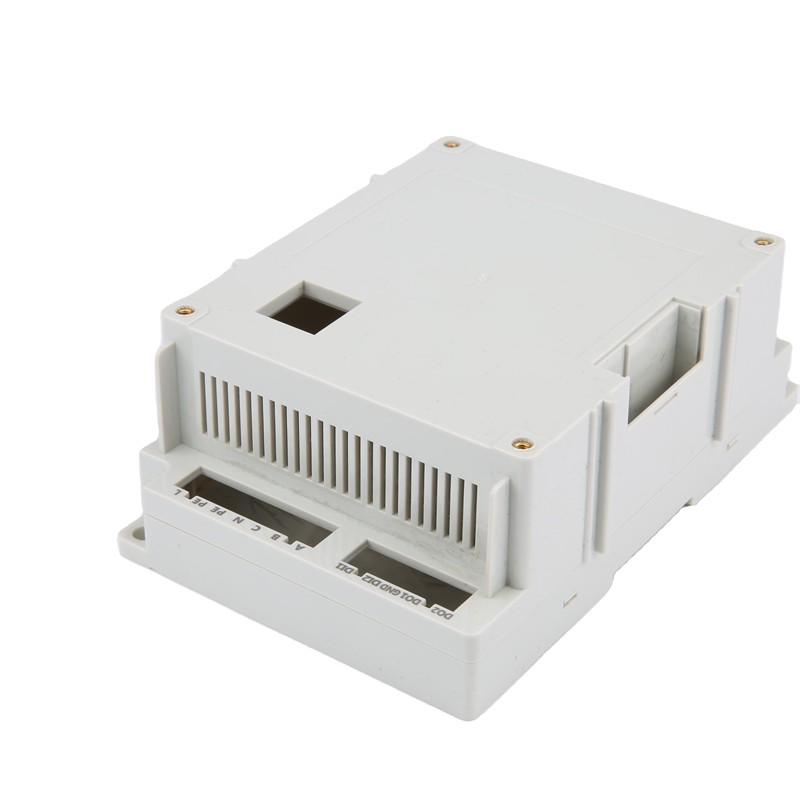
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More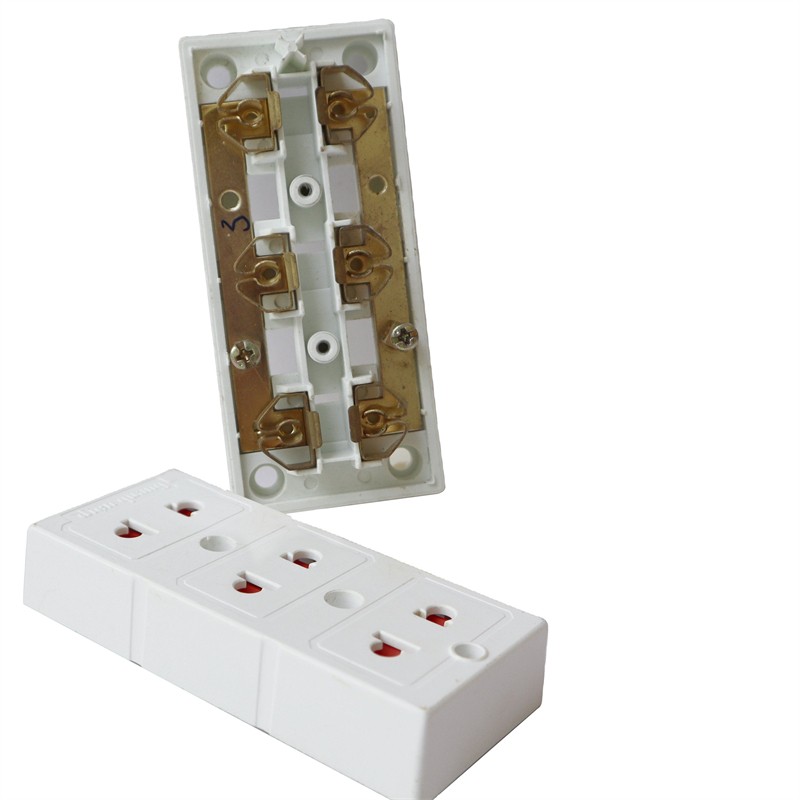
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More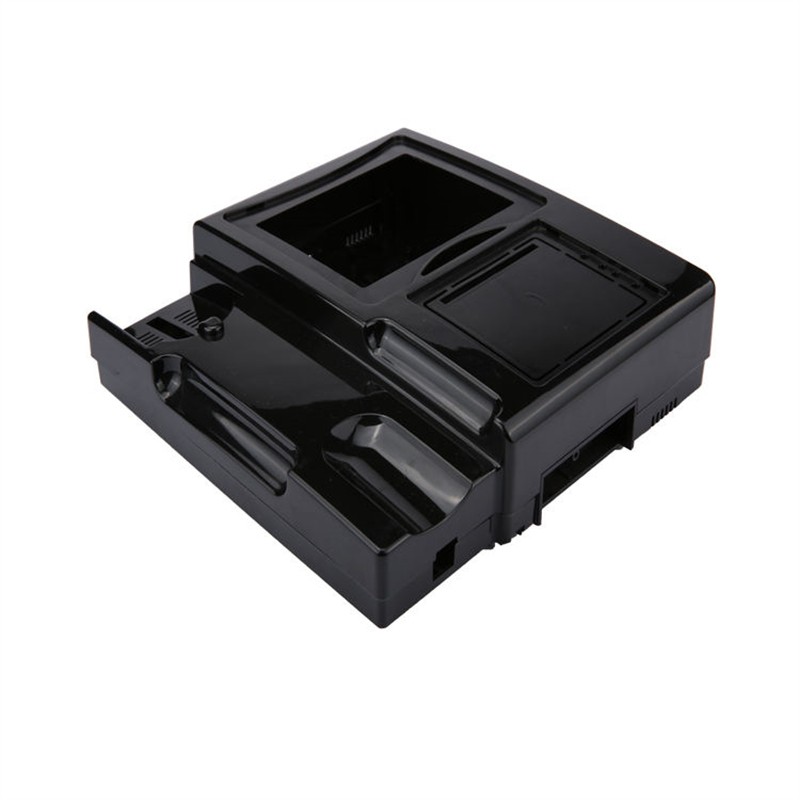
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More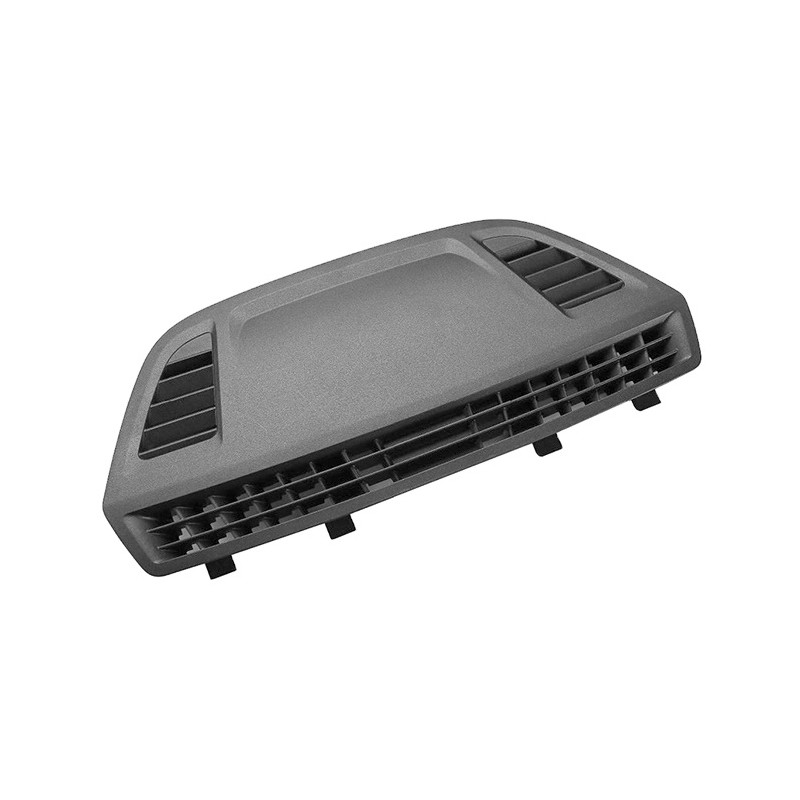
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More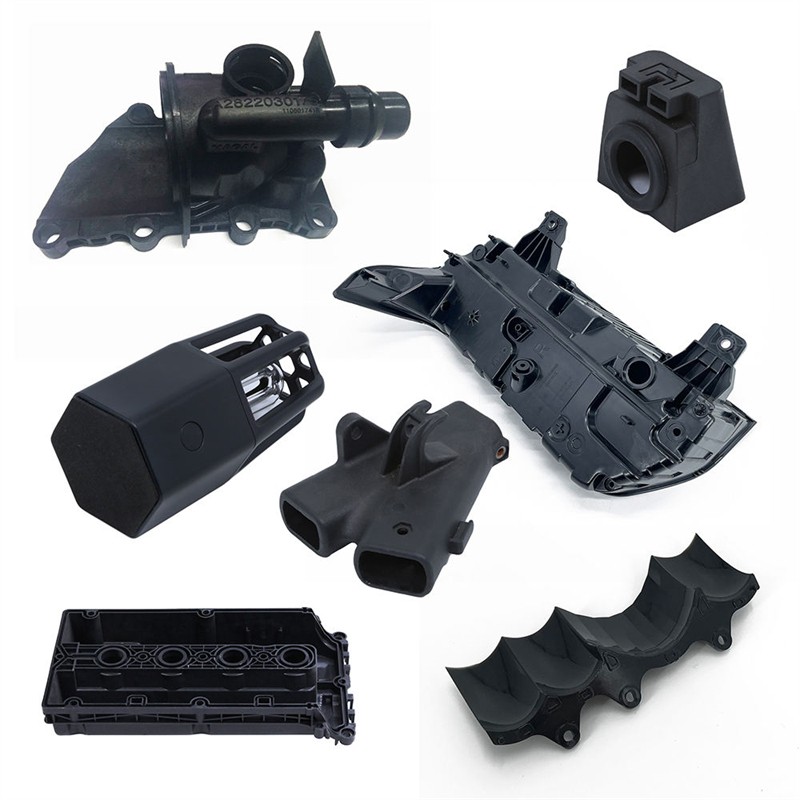
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More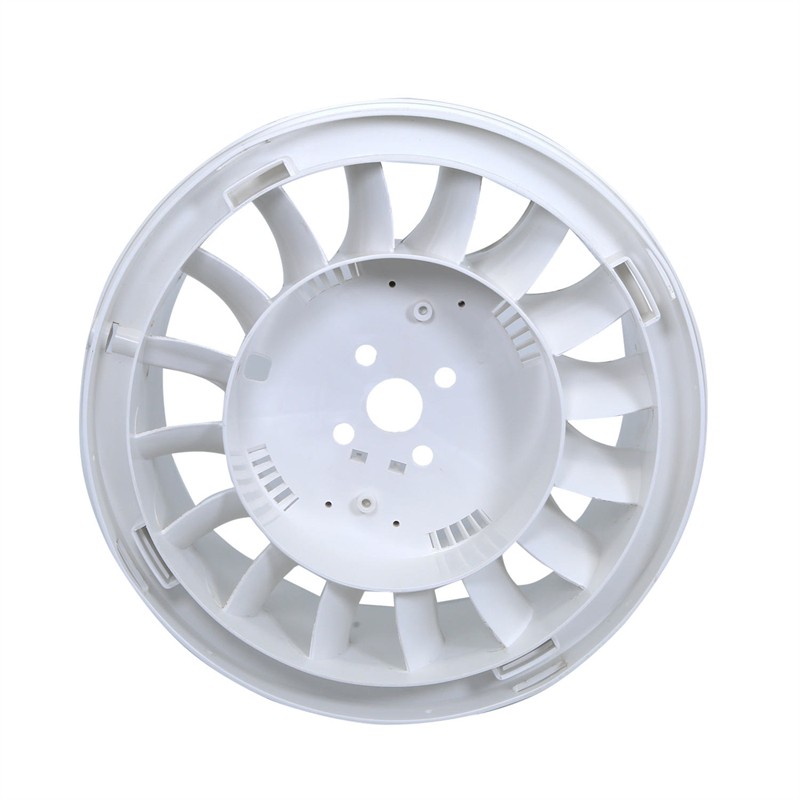
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More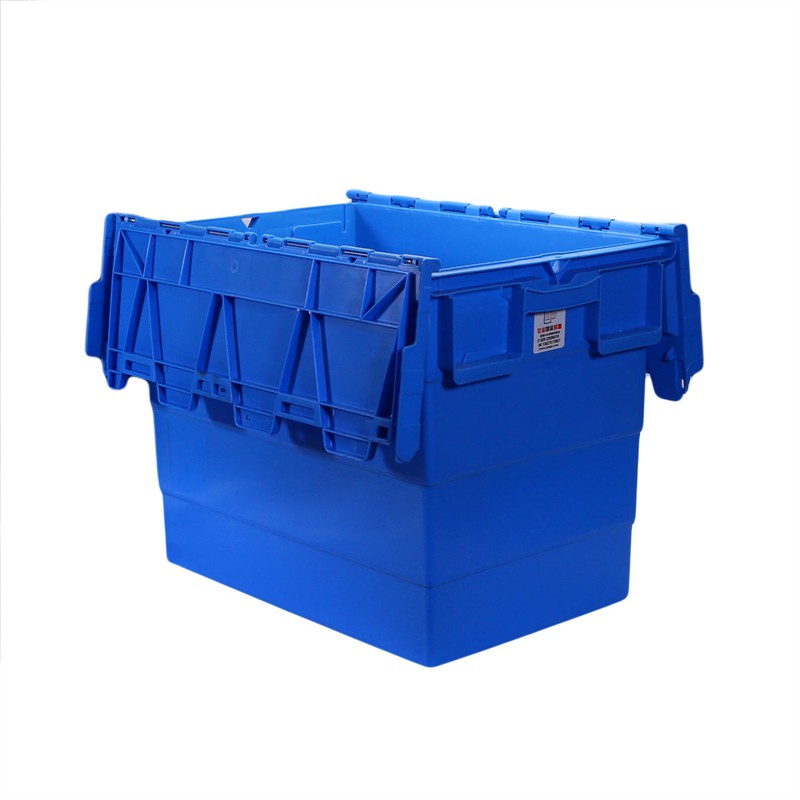
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More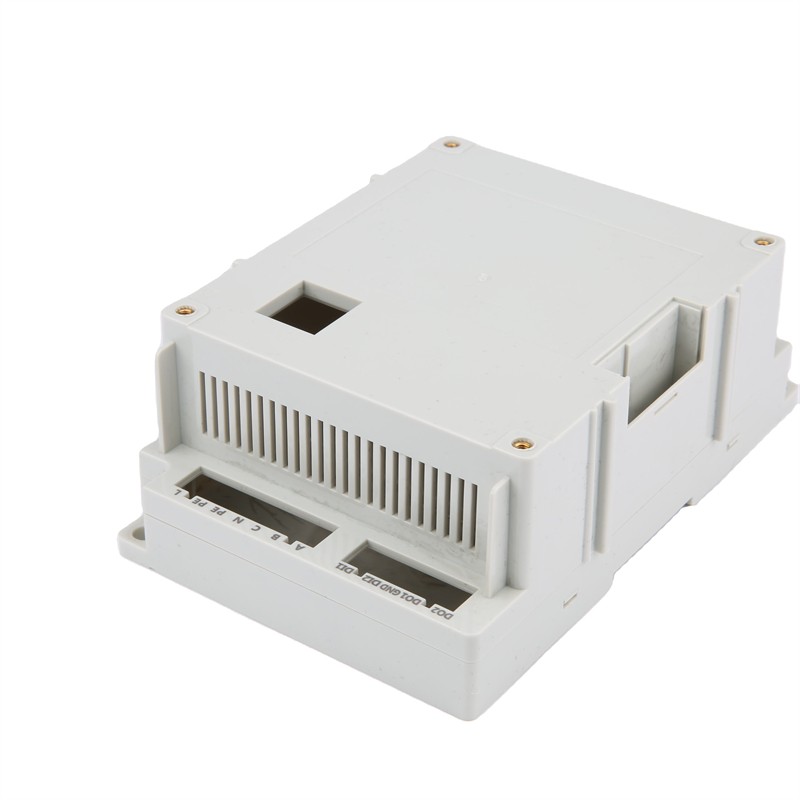
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.
Learn More Contact Us
Contact Us Address : No.103, Tong’an Park, Tong’an Industry Zone, Xiamen, China
Address : No.103, Tong’an Park, Tong’an Industry Zone, Xiamen, China WhatsApp : +86 18259211580
WhatsApp : +86 18259211580 Email : roger@ppl2009.com
Email : roger@ppl2009.com IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported




